Providing adequate care for a canine companion encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, from meeting basic biological needs to fostering a nurturing and stimulating environment. This includes providing nutritious food, fresh water, appropriate shelter, and regular veterinary care. Beyond the physical requirements, responsible pet ownership also involves understanding and addressing a dog’s social, emotional, and behavioral needs. For instance, regular exercise, mental stimulation through play and training, and socialization with other dogs and people are crucial for a dog’s overall well-being.
Commitment to proper canine care results in a mutually beneficial relationship. Dogs that receive appropriate care tend to be healthier, happier, and better-behaved companions. Historically, the relationship between humans and dogs has evolved from working partnerships to close companionship, increasing the emphasis on responsible care to ensure the animal’s physical and emotional health. This holistic approach recognizes the dog as a sentient being with complex needs, leading to improved welfare standards and a deeper understanding of the human-animal bond.
The subsequent sections will explore the multifaceted aspects of canine care in greater detail. Topics covered will include nutritional requirements, exercise recommendations, training techniques, healthcare essentials, and responsible pet ownership practices. This comprehensive guide aims to equip prospective and current dog owners with the knowledge and resources necessary to provide optimal care and cultivate a thriving relationship with their canine companions.
Essential Considerations for Canine Care
Proper canine care requires attention to various factors impacting a dog’s overall health and well-being. The following tips offer guidance on essential aspects of responsible dog ownership.
Tip 1: Nutritional Needs: Providing a balanced diet is fundamental. High-quality commercial dog food formulated for the dog’s age, breed, and activity level is recommended. Nutritional consultations with veterinarians can help address specific dietary needs or concerns.
Tip 2: Exercise and Enrichment: Regular physical activity and mental stimulation are crucial. Daily walks, playtime, and interactive toys prevent boredom and promote physical and mental health. Tailoring activities to the breed’s energy level is essential.
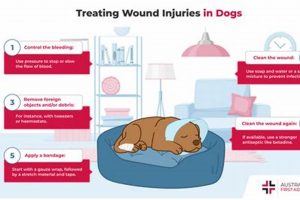
Tip 3: Veterinary Care: Preventative healthcare is vital. Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and parasite prevention are crucial for maintaining health and preventing disease. Addressing health concerns promptly is essential.
Tip 4: Training and Socialization: Consistent training and early socialization are key to a well-behaved dog. Positive reinforcement methods are recommended for effective training. Exposure to various environments, people, and other dogs helps develop appropriate social skills.
Tip 5: Shelter and Safety: Providing a safe and comfortable environment is essential. Access to fresh water, appropriate shelter from the elements, and a secure space are necessary. Protecting dogs from potential hazards within the home and environment is crucial.
Tip 6: Grooming and Hygiene: Regular grooming maintains hygiene and prevents health issues. Brushing, bathing, and nail trimming are essential components of routine care. Dental hygiene, including regular teeth cleaning, is also crucial.
Tip 7: Understanding Canine Behavior: Learning to interpret canine body language and communication signals is essential for effective interaction. Recognizing signs of stress, fear, or aggression helps prevent potential issues and promotes a harmonious relationship.
Implementing these tips ensures a dog’s physical and emotional well-being, fostering a strong and positive human-animal bond. Consistent care and attention contribute significantly to a dog’s overall quality of life.
In conclusion, responsible dog ownership entails a comprehensive approach that addresses a dog’s diverse needs. By understanding and fulfilling these requirements, one can ensure a fulfilling and enriching companionship.
1. Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in canine health and well-being, forming a cornerstone of responsible dog ownership. A balanced diet provides the necessary energy and building blocks for growth, tissue repair, and overall physiological function. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to a range of health issues, including stunted growth, weakened immune systems, and organ dysfunction. Conversely, proper nutrition contributes significantly to a dog’s vitality, promoting healthy skin and coat, strong bones, and optimal energy levels. For instance, a diet rich in calcium and phosphorus supports skeletal development in puppies, while adequate protein intake maintains muscle mass in adult dogs. The specific nutritional requirements vary depending on factors such as age, breed, activity level, and health status. Feeding a diet tailored to these individual needs ensures optimal health outcomes.
Practical application of nutritional principles involves selecting appropriate dog food and understanding feeding guidelines. High-quality commercial dog food, formulated to meet specific life-stage requirements, offers a convenient and balanced nutritional solution. Consulting a veterinarian can provide further guidance on selecting the best diet for individual dogs. Dietary adjustments might be necessary for dogs with specific health conditions, such as allergies or digestive sensitivities. Understanding ingredient lists and nutritional labels empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog’s diet. Furthermore, portion control is essential to prevent obesity, a common health problem in dogs with significant health implications. Monitoring a dog’s weight and adjusting food intake as needed helps maintain a healthy body condition.
In summary, proper nutrition is not merely a component of responsible dog ownership but a fundamental requirement for ensuring a dog’s overall health and longevity. Providing a balanced diet tailored to individual needs forms the basis for a healthy life, contributing to increased vitality, disease prevention, and enhanced quality of life. Addressing nutritional needs effectively requires understanding dietary principles, selecting appropriate food, and practicing responsible feeding habits. This proactive approach to nutrition translates directly into a healthier, happier, and more resilient canine companion.
2. Shelter
Providing adequate shelter is a fundamental aspect of responsible canine care. Shelter protects dogs from the elements, ensuring their safety, comfort, and overall well-being. A suitable shelter contributes significantly to a dog’s physical and psychological health, mitigating the risks associated with extreme temperatures, inclement weather, and environmental hazards. The type of shelter required varies depending on factors such as climate, breed, and individual needs.
- Protection from the Elements:
Shelter provides crucial protection from extreme heat, cold, rain, snow, and wind. Exposure to harsh weather conditions can lead to hypothermia, heatstroke, and other health problems. For example, a dog housed outdoors in freezing temperatures requires insulated shelter to maintain body temperature. Similarly, shade and ventilation are crucial in hot climates to prevent overheating.
- Safety and Security:
A secure shelter offers a safe haven from potential dangers, including predators, traffic, and other environmental hazards. A fenced yard provides a secure outdoor space for exercise and play, while a kennel or indoor crate offers a safe and comfortable resting area. This sense of security also contributes to a dog’s psychological well-being, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Rest and Recuperation:
Shelter provides a dedicated space for rest and recuperation, essential for maintaining physical and mental health. A comfortable bed or resting area allows dogs to relax and sleep undisturbed. Adequate rest contributes to a dog’s overall health, supporting immune function, cognitive function, and emotional stability.
- Behavioral Considerations:
Providing appropriate shelter can also address behavioral needs. For example, a dog prone to anxiety may benefit from a den-like space that provides a sense of security and privacy. Similarly, a designated resting area can help establish routines and prevent destructive behaviors associated with boredom or stress. Proper shelter, therefore, contributes to a more harmonious household environment.
In conclusion, providing suitable shelter is an integral part of responsible dog ownership. By considering the various facets of shelter protection from the elements, safety and security, rest and recuperation, and behavioral needs owners can ensure their canine companions thrive in a safe, comfortable, and enriching environment. This commitment to providing adequate shelter directly contributes to a dogs overall health, well-being, and quality of life.
3. Health Care
Canine health care forms a cornerstone of responsible dog ownership, directly impacting a dog’s quality of life and longevity. Proactive health management, encompassing preventative care and timely intervention for illness or injury, is crucial. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of serious health issues, contributing to a longer, healthier life. Neglecting health care can lead to preventable diseases, chronic conditions, and decreased quality of life. For instance, routine vaccinations protect against potentially fatal diseases like parvovirus and distemper. Regular parasite prevention safeguards against heartworm, fleas, and ticks, which can transmit diseases and cause discomfort. Dental care, often overlooked, plays a significant role in overall health. Periodontal disease, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss, pain, and even systemic infections.
Practical application of canine health care involves regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, parasite prevention, and dental hygiene. Annual or bi-annual veterinary visits allow for early detection of potential health problems. Veterinarians can assess a dog’s overall health, recommend appropriate vaccinations and parasite prevention protocols, and address any specific health concerns. Owners play a crucial role in observing their dogs for any changes in behavior, appetite, or physical condition. Promptly addressing these changes and seeking veterinary advice when necessary allows for early intervention and better health outcomes. For example, noticing changes in a dog’s eating habits or energy levels could indicate an underlying health issue requiring veterinary attention. Early diagnosis and treatment often lead to more favorable prognoses and improved long-term health.
In summary, prioritizing canine health care is not merely a responsibility but an investment in a dog’s well-being. Preventative measures, combined with timely veterinary intervention, safeguard against preventable diseases and contribute significantly to a dog’s overall health and longevity. Understanding the significance of health care and actively participating in a dog’s health management ensures a higher quality of life and strengthens the human-animal bond. This commitment to proactive health care translates directly into a healthier, happier, and more resilient canine companion.
4. Exercise and Enrichment
Exercise and enrichment are integral components of responsible canine care, directly influencing a dog’s physical and mental well-being. Adequate physical activity and mental stimulation are essential for maintaining a healthy weight, preventing behavioral problems, and promoting overall health and happiness. These activities fulfill innate canine needs, contributing significantly to a dog’s quality of life.
- Physical Exercise:
Physical exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthens muscles and bones, and improves cardiovascular health. Daily walks, runs, or playtime in a securely fenced area provide necessary outlets for physical energy. The type and duration of exercise should be tailored to the dog’s breed, age, and health status. For example, high-energy breeds like Border Collies require significantly more exercise than lower-energy breeds like Bulldogs. Insufficient exercise can lead to obesity, behavioral problems, and frustration.
- Mental Stimulation:
Mental enrichment prevents boredom and reduces the risk of destructive behaviors. Puzzle toys, interactive games, and training sessions provide mental stimulation, challenging a dog’s cognitive abilities. For instance, puzzle toys that dispense treats encourage problem-solving skills. Training sessions reinforce basic commands and provide mental engagement. A lack of mental stimulation can lead to anxiety, destructive chewing, and excessive barking.
- Social Interaction:
Social interaction with other dogs and people is crucial for proper social development. Regular opportunities for socialization, such as visits to dog parks or organized playgroups, help dogs develop appropriate social skills. Socialization is particularly important during puppyhood, but it remains beneficial throughout a dog’s life. Lack of socialization can lead to fear, aggression, and difficulty interacting with other dogs or people.
- Environmental Enrichment:
Providing a stimulating environment contributes to a dog’s overall well-being. Access to a variety of toys, rotating toys regularly, and providing opportunities for exploration within a safe environment prevent boredom and promote mental engagement. For example, providing a variety of chew toys can satisfy a dog’s natural chewing instincts and prevent destructive chewing on furniture. A stimulating environment contributes to a happier and more well-adjusted dog.
In conclusion, exercise and enrichment are not merely optional activities but essential requirements for responsible canine care. Addressing these needs directly impacts a dog’s physical health, mental well-being, and behavioral development. Providing adequate exercise, mental stimulation, social interaction, and a stimulating environment contributes significantly to a fulfilling and enriching life for canine companions. This holistic approach to care strengthens the human-animal bond and promotes a harmonious relationship between humans and their canine companions.
5. Training and Socialization
Training and socialization are fundamental pillars of responsible canine care, inextricably linked to a dog’s overall well-being and successful integration into human society. These interconnected processes shape behavior, promote positive interactions, and contribute significantly to a harmonious relationship between dogs and their human companions. Effective training establishes clear communication and boundaries, while proper socialization equips dogs with the skills necessary to navigate social situations confidently and appropriately. Neglecting these crucial aspects can lead to behavioral problems, anxiety, and difficulty interacting with other dogs and people, impacting both the dog’s quality of life and the owner’s experience.
- Basic Obedience Training:
Basic obedience training forms the foundation for a well-behaved dog, establishing clear expectations and facilitating communication between dog and owner. Commands such as “sit,” “stay,” “come,” and “leave it” provide essential control and guidance, promoting safety and preventing undesirable behaviors. For example, a reliable recall (“come”) can prevent a dog from running into traffic or other dangerous situations. Consistent obedience training strengthens the human-animal bond, fostering mutual respect and understanding.
- Socialization with Dogs and People:
Early and ongoing socialization is crucial for developing appropriate social skills. Exposing dogs to a variety of people, dogs, environments, and situations helps them learn to interact confidently and appropriately. Puppy classes and controlled playgroups provide safe environments for socialization, allowing dogs to learn canine communication and social etiquette. Proper socialization minimizes the risk of fear-based aggression, reactivity, and anxiety, promoting well-adjusted behavior in various social contexts.
- Addressing Problem Behaviors:
Training plays a vital role in addressing and modifying problem behaviors. Excessive barking, destructive chewing, and jumping can be addressed through consistent training and behavior modification techniques. Positive reinforcement methods, focusing on rewarding desired behaviors, are generally more effective than punishment-based approaches. Consulting a certified professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide tailored guidance for addressing specific behavioral challenges, promoting positive change and enhancing the human-animal bond.
- Lifelong Learning and Enrichment:
Training and socialization are not limited to puppyhood; they should continue throughout a dog’s life. Ongoing training provides mental stimulation, reinforces learned behaviors, and strengthens the bond between dog and owner. Introducing new commands, tricks, or activities keeps dogs mentally engaged and prevents boredom. Continued socialization ensures dogs maintain their social skills and adapt to new situations confidently. This commitment to lifelong learning and enrichment contributes significantly to a dog’s overall well-being and quality of life.
In conclusion, training and socialization are not merely components of responsible dog ownership but essential investments in a dog’s overall well-being. These interconnected processes shape behavior, promote positive interactions, and enhance the human-animal bond. By prioritizing training and socialization, owners equip their canine companions with the skills necessary to thrive in human society, fostering a harmonious and fulfilling relationship for both dog and owner. This commitment translates directly into a well-behaved, well-adjusted, and happy canine companion.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Care
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the essential requirements for providing optimal canine care. Understanding these fundamental aspects is crucial for prospective and current dog owners.
Question 1: What constitutes a balanced diet for a dog?
A balanced canine diet provides essential nutrients in appropriate proportions. This includes proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Commercial dog food formulated for specific life stages often provides a balanced nutritional profile. Consulting a veterinarian can assist in determining the most suitable dietary plan for individual needs.
Question 2: How much exercise does a dog require daily?
Exercise requirements vary depending on breed, age, and health status. Most dogs benefit from at least 30 minutes to an hour of exercise daily. This can include walks, runs, playtime, or engaging in canine sports. Tailoring the intensity and duration of exercise to individual needs is crucial.
Question 3: How often should veterinary check-ups be scheduled?
Generally, annual veterinary check-ups are recommended for healthy adult dogs. Puppies and senior dogs may require more frequent visits. Regular check-ups allow for early disease detection, preventative care, and addressing any health concerns promptly.
Question 4: When should socialization begin for a puppy?
Socialization should begin as early as possible, ideally during puppyhood. Exposing puppies to various sights, sounds, people, and other dogs in a controlled and positive manner helps them develop appropriate social skills and reduces the risk of behavioral problems later in life.
Question 5: What are the essential components of a safe and comfortable shelter for a dog?
Essential components include protection from the elements, a comfortable resting area, and a sense of security. Access to fresh water and appropriate ventilation are also crucial. The specific shelter requirements may vary depending on the climate and the dog’s individual needs.
Question 6: How can one identify signs of illness or distress in a dog?
Changes in behavior, appetite, energy levels, or elimination habits can indicate potential health problems. Unexplained weight loss or gain, excessive panting, vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in coat condition warrant veterinary attention. Promptly addressing these signs is essential for ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Addressing these common inquiries provides a foundation for understanding the fundamental aspects of responsible canine care. Further research and consultation with veterinary professionals can provide additional guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
The next section delves further into specific aspects of canine care, offering practical tips and in-depth information for ensuring a dog’s overall well-being.
Meeting the Comprehensive Needs of Canine Companions
Successfully addressing the multifaceted requirements of canine care necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their physical, emotional, and social needs. This exploration has highlighted key elements, including providing balanced nutrition, appropriate shelter, regular healthcare, ample exercise and enrichment, and consistent training and socialization. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring a dog’s overall health, well-being, and successful integration into human society. Neglecting any of these aspects can have detrimental effects on a dog’s physical or mental health, impacting both the animal’s quality of life and the human-animal bond.
Ultimately, responsible canine care transcends merely meeting basic survival needs; it represents a commitment to providing a fulfilling and enriching life for a sentient being. This commitment requires continuous learning, adaptation to individual needs, and a proactive approach to health and well-being. The welfare of canine companions rests on the understanding and consistent application of these fundamental principles, leading to a stronger human-animal bond and a more harmonious coexistence.