Providing essential care for a canine companion encompasses numerous responsibilities, ranging from meeting basic physical needs to ensuring mental and emotional well-being. This includes providing nutritious food, fresh water, regular exercise, a safe and comfortable shelter, and consistent training. For example, a balanced diet tailored to the dog’s age, breed, and activity level is crucial for maintaining healthy weight, strong bones, and a vibrant coat.
Responsible canine care yields numerous benefits, not only for the animal but also for the owner and the wider community. A well-cared-for dog is typically healthier, happier, and better behaved, reducing the likelihood of veterinary expenses, behavioral problems, and potential conflicts with others. Historically, the relationship between humans and dogs has evolved from working partnerships to close companionship, underscoring the inherent value placed on their well-being. This historical context emphasizes the ethical obligation to provide appropriate care for domesticated animals.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of canine care is essential for prospective and current dog owners. The following sections will delve into specific aspects of responsible dog ownership, offering practical guidance and expert advice on nutrition, exercise, training, healthcare, grooming, and creating a stimulating and enriching environment.
Essential Canine Care Tips
Implementing proactive measures ensures a dog’s physical health, mental stimulation, and overall well-being. These tips offer practical guidance for responsible canine ownership.
Tip 1: Nutritional Provision: A balanced diet, tailored to the dog’s breed, age, and activity level, forms the cornerstone of good health. High-quality commercial dog food, supplemented with occasional healthy treats, typically provides necessary nutrients. Fresh water should always be accessible.
Tip 2: Exercise and Enrichment: Regular physical activity, including walks, runs, and playtime, is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing behavioral issues. Mental stimulation through interactive toys and puzzles prevents boredom and promotes cognitive function.
Tip 3: Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary checkups, vaccinations, and preventative treatments protect against diseases and parasites. Prompt attention to any signs of illness or injury is vital.
Tip 4: Grooming and Hygiene: Regular brushing removes loose hair and prevents matting. Bathing, nail trimming, and dental care contribute to overall hygiene and comfort.
Tip 5: Safe and Comfortable Shelter: Providing a safe, clean, and comfortable living environment is paramount. This includes a designated sleeping area, protection from the elements, and a secure space free from hazards.
Tip 6: Training and Socialization: Consistent training establishes clear boundaries and fosters desirable behaviors. Early socialization with other dogs and people promotes confident and well-adjusted interactions.
Tip 7: Identification and Safety: Microchipping provides permanent identification in case of separation. A collar with identification tags and a secure leash are essential safety measures during walks and outings.
Adhering to these guidelines contributes significantly to a dog’s quality of life, fostering a strong bond between canine companions and their human caregivers.
By understanding and addressing these core aspects of canine care, one can ensure a fulfilling and rewarding relationship with a canine companion.
1. Nutrition
Nutrition forms a cornerstone of canine care, directly impacting a dog’s health, longevity, and overall well-being. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients for growth, energy, immune function, and organ health. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to a range of health problems, including stunted growth, weakened immune systems, skin conditions, and digestive issues. Conversely, proper nutrition contributes to a shiny coat, healthy weight, strong bones, and increased energy levels. For example, a diet rich in high-quality protein supports muscle development and repair, while essential fatty acids contribute to healthy skin and coat. The correct balance of vitamins and minerals ensures proper organ function and strengthens the immune system.
Practical application of nutritional principles requires consideration of a dog’s age, breed, activity level, and any existing health conditions. Puppies require diets formulated for growth, while senior dogs benefit from formulations that support joint health and address age-related changes in metabolism. Active breeds may require higher calorie intakes compared to less active breeds. Dietary adjustments may also be necessary for dogs with specific health conditions, such as allergies or diabetes. Consulting a veterinarian can provide tailored guidance on selecting appropriate food and portion sizes. Furthermore, understanding ingredient lists and recognizing potentially harmful additives empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog’s nutritional intake.
In summary, providing optimal nutrition is a critical component of responsible dog ownership. A well-nourished dog is more likely to thrive, exhibiting increased energy levels, a robust immune system, and a healthy physique. Understanding the link between nutrition and overall well-being enables owners to make informed decisions, promoting a longer, healthier, and happier life for their canine companions. Ignoring nutritional needs can result in significant health problems, impacting both the dog’s quality of life and the owner’s financial burden. Therefore, prioritizing nutrition represents a significant investment in a dog’s long-term health and happiness.
2. Shelter
Providing adequate shelter is a fundamental aspect of responsible dog ownership, directly impacting a dog’s physical and psychological well-being. Shelter provides protection from the elements, a safe haven for rest and relaxation, and a sense of security essential for reducing stress and promoting overall health. A suitable shelter caters to a dog’s instinctual need for denning and contributes significantly to a balanced and fulfilling life.
- Protection from the Elements
Exposure to extreme temperatures, precipitation, and direct sunlight can pose significant health risks to dogs. Appropriate shelter mitigates these risks by providing a temperature-regulated environment. For example, a well-insulated dog house protects against both winter cold and summer heat. Access to shade during hot weather prevents heatstroke, while a dry, draft-free space safeguards against hypothermia in colder climates. These provisions are crucial for maintaining a dog’s core body temperature and preventing weather-related illnesses.
- Safety and Security
A secure shelter provides a safe haven from potential dangers, including predators, traffic, and other environmental hazards. A fenced yard offers a controlled environment for exercise and exploration, while a secure kennel or indoor space prevents escapes and protects against potential harm. This sense of security reduces anxiety and promotes a calm and relaxed demeanor. For instance, a fearful dog may find solace in a crate or den-like space, providing a sense of control and predictability.
- Rest and Relaxation
Adequate rest is crucial for a dog’s physical and mental health. A comfortable and quiet sleeping area allows for uninterrupted rest, promoting restorative sleep cycles and reducing stress. Providing a designated sleeping space, such as a dog bed or a comfortable blanket, encourages a sense of routine and contributes to a dog’s overall well-being. This dedicated space allows dogs to retreat and decompress, mirroring their natural denning instincts.
- Behavioral Benefits
Providing appropriate shelter can positively influence a dog’s behavior. A secure and predictable environment reduces anxiety and destructive behaviors often associated with stress and insecurity. A designated space also aids in housetraining by providing a clear distinction between indoor and outdoor areas. Furthermore, a comfortable and secure shelter can mitigate separation anxiety by providing a safe and familiar space during periods of owner absence.
In conclusion, providing suitable shelter is not simply a matter of convenience; it is a fundamental requirement for responsible dog ownership. Addressing these facets of shelter contributes significantly to a dog’s overall health, happiness, and behavioral well-being. Neglecting this essential aspect of care can lead to health problems, behavioral issues, and a diminished quality of life. Therefore, investing in appropriate shelter demonstrates a commitment to providing a safe, secure, and nurturing environment for a canine companion.
3. Exercise
Exercise is integral to responsible canine care, directly influencing a dog’s physical and mental well-being. A lack of sufficient exercise can lead to a cascade of health problems, including obesity, joint issues, cardiovascular disease, and behavioral problems such as excessive barking, destructive chewing, and anxiety. Conversely, regular physical activity strengthens muscles, improves cardiovascular health, helps maintain a healthy weight, and promotes mental stimulation, reducing the risk of these issues. For instance, a daily walk or run provides essential cardiovascular exercise, while playtime with interactive toys offers mental enrichment and strengthens the bond between dog and owner.
The type and amount of exercise required vary based on factors such as breed, age, and individual health conditions. High-energy breeds, like Border Collies or Australian Shepherds, often require more vigorous exercise than smaller, less active breeds. Puppies and senior dogs benefit from shorter, less strenuous activities tailored to their physical capabilities. Dogs with specific health conditions, such as hip dysplasia or heart problems, require exercise regimens adapted to their limitations. Consulting a veterinarian can provide guidance on developing a safe and effective exercise plan. Furthermore, incorporating variety into exercise routines keeps dogs engaged and mentally stimulated. Activities such as swimming, hiking, or playing fetch provide physical challenges and mental enrichment, promoting overall well-being.
In summary, prioritizing regular exercise is not merely a recommendation but a crucial component of responsible dog ownership. Adequate physical activity directly contributes to a dog’s physical health, mental well-being, and behavioral balance. Understanding the specific exercise needs of individual dogs, considering factors such as breed, age, and health status, allows owners to develop tailored exercise plans that promote a healthy and fulfilling life. Neglecting this essential aspect of care can lead to a decline in both physical and mental health, significantly impacting a dog’s quality of life. Therefore, incorporating consistent and appropriate exercise into a dog’s routine represents a critical investment in its long-term health and happiness.
4. Healthcare
Healthcare represents a critical component within the broader context of responsible canine care. Proactive healthcare measures contribute significantly to a dog’s overall well-being, longevity, and quality of life. Addressing healthcare needs not only prevents disease and mitigates suffering but also strengthens the human-animal bond through proactive engagement and attentive care.
- Preventative Care
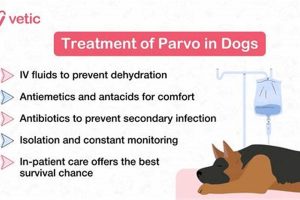
Preventative care forms the foundation of responsible canine healthcare. This encompasses regular vaccinations against common canine diseases such as rabies, distemper, and parvovirus. Parasite prevention, through regular administration of flea, tick, and heartworm medications, safeguards against infestations and potential transmission of vector-borne diseases. Routine veterinary checkups facilitate early detection of potential health issues, allowing for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes. For example, annual dental cleanings prevent periodontal disease, a common ailment in dogs that can lead to tooth loss and other systemic health problems. These preventative measures minimize the risk of serious illness and contribute significantly to a dog’s long-term health.
- Diagnosis and Treatment
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of illnesses and injuries are essential for minimizing suffering and promoting recovery. Recognizing signs of illness, such as changes in appetite, lethargy, vomiting, or diarrhea, warrants immediate veterinary attention. Diagnostic testing, including blood work, urinalysis, and imaging, enables accurate diagnosis and informs treatment plans. Treatment options may include medications, surgery, or other therapeutic interventions. For instance, early detection and treatment of a urinary tract infection can prevent its progression to a more serious kidney infection. Swift action in cases of injury, such as a fractured bone, minimizes pain and promotes healing.
- Emergency Care
Preparation for potential emergencies is a crucial aspect of responsible dog ownership. Knowing the location of the nearest 24-hour emergency veterinary clinic and having a plan in place for transportation ensures timely access to critical care in life-threatening situations. Understanding basic first-aid procedures for dogs, such as how to control bleeding or stabilize a fracture, can be life-saving in emergency situations. For example, knowing how to perform CPR on a dog can be crucial in cases of cardiac arrest. Preparation for emergencies provides peace of mind and equips owners to respond effectively in critical situations.
- Long-Term Health Management
Managing chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, arthritis, or allergies, requires ongoing veterinary care and owner commitment. This may involve regular medication administration, dietary adjustments, physical therapy, or other specialized treatments. Consistent monitoring of a dog’s health status, including regular blood work and physical examinations, enables adjustments to treatment plans as needed. For example, a dog with diabetes requires regular insulin injections and blood glucose monitoring to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Diligent management of chronic conditions improves a dog’s quality of life and extends lifespan.
In conclusion, healthcare is an interwoven and indispensable element of responsible canine care. Prioritizing preventative care, seeking prompt diagnosis and treatment, preparing for emergencies, and diligently managing chronic conditions contribute significantly to a dog’s overall health, well-being, and longevity. Integrating these facets of healthcare into a comprehensive care plan demonstrates a commitment to providing a high quality of life for a canine companion. Neglecting healthcare needs can result in preventable suffering, decreased lifespan, and diminished quality of life. Therefore, proactive engagement with healthcare represents a crucial investment in a dog’s long-term health and happiness.
5. Training
Training is an indispensable element of responsible canine care, inextricably linked to a dog’s overall well-being and successful integration into human society. Effective training establishes clear communication between dog and owner, fostering a relationship built on mutual understanding and respect. This connection promotes desirable behaviors, mitigates undesirable ones, and enhances the safety and well-being of both the dog and the surrounding community. Furthermore, training provides mental stimulation, which is crucial for preventing boredom and associated behavioral problems. For example, teaching a dog basic obedience commands, such as “sit,” “stay,” and “come,” provides structure and predictability, reducing anxiety and promoting a sense of security. A well-trained dog is more likely to be a welcomed member of the family and community, enhancing the quality of life for both the dog and its human companions.
The practical significance of training extends beyond basic obedience. Socialization, a critical component of training, exposes dogs to a variety of people, places, and situations, fostering confident and adaptable behavior. Early socialization minimizes the risk of fear-based aggression and reactivity, promoting positive interactions with other dogs and humans. Specialized training, such as agility or scent work, provides further mental and physical enrichment, channeling a dog’s natural instincts and preventing behavioral issues stemming from boredom or frustration. For instance, a dog trained in agility learns to navigate obstacles and follow commands, developing problem-solving skills and strengthening the bond with its handler. These activities provide outlets for physical and mental energy, leading to a more balanced and well-adjusted canine companion.
In conclusion, training is not merely a desirable addition but a fundamental aspect of responsible canine care. It establishes a framework for clear communication, fosters desirable behaviors, promotes socialization, and provides essential mental stimulation. These factors contribute significantly to a dog’s overall well-being, safety, and successful integration into human society. Neglecting training can lead to behavioral problems, strained relationships, and compromised safety. Therefore, investing time and effort in training represents a crucial investment in a dog’s long-term well-being and the harmonious coexistence of humans and their canine companions. This commitment fosters a stronger bond, enhances communication, and cultivates a relationship built on mutual respect and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Care
Addressing common queries regarding essential canine care provides clarity and guidance for responsible dog ownership. These frequently asked questions offer practical insights into various aspects of canine well-being.
Question 1: What constitutes a balanced diet for a dog?
A balanced canine diet comprises high-quality protein, healthy fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Specific nutritional requirements vary based on breed, age, activity level, and health status. Consulting a veterinarian can assist in determining appropriate dietary choices.
Question 2: How much exercise does a dog require daily?
Exercise requirements vary based on breed, age, and individual health conditions. Most dogs benefit from at least 30 minutes to an hour of exercise daily, which can include walks, runs, playtime, or other physical activities.
Question 3: How frequently should veterinary checkups be scheduled?
Generally, annual veterinary checkups are recommended for healthy adult dogs. Puppies and senior dogs, or those with existing health conditions, may require more frequent visits.
Question 4: What are essential grooming practices for dogs?
Essential grooming practices include regular brushing, bathing, nail trimming, and dental care. The frequency of these activities varies based on breed and individual coat type.
Question 5: How can one create a safe and stimulating environment for a dog?
A safe and stimulating environment provides opportunities for physical activity, mental enrichment, and social interaction. This can include access to a secure outdoor space, interactive toys, and regular playtime with other dogs and humans.
Question 6: What are the key components of effective dog training?
Effective dog training utilizes positive reinforcement methods, consistent application of rules, and early socialization. Professional guidance can assist in developing effective training strategies.
Addressing these common questions provides a foundation for understanding the core principles of canine care. Further research and consultation with veterinary professionals can offer tailored guidance based on individual dog needs.
This information provides a starting point for navigating the responsibilities of dog ownership. The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of canine care, offering practical guidance and expert advice.
Conclusion
Meeting the comprehensive needs of a canine companion encompasses a multifaceted approach, encompassing nutritional provision, shelter, exercise, healthcare, and training. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring a dog’s physical health, mental well-being, and successful integration into human society. Prioritizing a balanced diet fuels optimal growth and energy levels. Providing safe and comfortable shelter offers protection and fosters a sense of security. Regular exercise maintains physical fitness and stimulates mental acuity. Proactive healthcare safeguards against disease and promotes longevity. Consistent training cultivates desirable behaviors and strengthens the human-animal bond.
Commitment to these fundamental aspects of care reflects a profound responsibility inherent in dog ownership. This dedication not only enriches the lives of canine companions but also fosters a harmonious coexistence within the broader community. Continued learning and adaptation to the evolving needs of individual dogs ensures a lifelong commitment to their well-being and underscores the enduring value of the human-animal partnership.