Caring for a female dog during her estrus cycle involves managing hygiene, behavior, and preventing unwanted pregnancies. This typically includes containing the dog to prevent mating, managing bleeding with appropriate pet hygiene products, and providing extra attention and comfort as she may exhibit mood changes.
Proper estrus management is crucial for canine health and well-being. Preventing unintended litters helps control pet overpopulation and reduces the strain on animal shelters. Furthermore, attentive care during this time can minimize stress for the dog and maintain a harmonious household environment. While spaying is a common and effective solution to eliminate estrus cycles, its not always immediately feasible or desired by all owners. Thus, understanding how to manage the cycle is essential for responsible dog ownership.
This information will cover various aspects of canine estrus care, including hygiene practices, behavioral management techniques, and strategies for preventing mating. It will also address common concerns and questions owners have about this period in their dog’s life.
Tips for Canine Estrus Care
The following tips offer practical guidance for managing a dog’s estrus cycle, promoting hygiene, and preventing unwanted pregnancies.
Tip 1: Confine the dog indoors or in a securely fenced area. This prevents contact with male dogs and minimizes the risk of mating. Supervise outdoor time closely.
Tip 2: Utilize dog diapers or sanitary pants. These products help manage bleeding and keep the home clean. Change them regularly to maintain hygiene.
Tip 3: Clean bedding and furniture frequently. Wash any soiled items thoroughly to eliminate odors and maintain a sanitary environment.
Tip 4: Offer extra attention and comfort. Dogs may experience mood changes during estrus. Provide a calm and supportive environment with familiar toys and bedding.
Tip 5: Avoid dog parks and other areas where male dogs congregate. This minimizes the chances of unwanted encounters and potential mating.
Tip 6: Be mindful of behavioral changes. Some dogs may become more clingy or anxious, while others might display increased aggression. Understanding these changes allows for appropriate responses and management.
Tip 7: Consult a veterinarian. If any unusual or concerning behaviors or physical symptoms arise, veterinary consultation is recommended to rule out any underlying health issues.
Implementing these tips contributes significantly to a dog’s well-being during estrus, promoting hygiene and preventing unwanted pregnancies. This approach supports a comfortable and stress-free experience for both the dog and the owner.
By understanding and implementing these strategies, responsible pet ownership is demonstrated, contributing to overall canine welfare and population control. This knowledge empowers owners to navigate this natural process effectively.
1. Hygiene
Hygiene plays a crucial role in caring for a dog during estrus. The vulva swells and discharges blood during this period, creating potential hygiene challenges. Without proper care, this discharge can stain furniture, bedding, and the dog’s fur. Furthermore, the vulva’s increased exposure to the environment elevates the risk of bacterial infections. For example, if a dog licks excessively to clean herself, she may inadvertently introduce bacteria, leading to inflammation or infection. Proper hygiene practices mitigate these risks.
Effective hygiene management involves regularly changing absorbent pads or dog diapers designed specifically for estrus. These products contain the discharge, preventing soiling and minimizing the dog’s urge to lick excessively. Frequent cleaning of the dog’s bedding and any soiled areas in the house is essential to maintain a sanitary environment and reduce odor. Using pet-safe cleaning solutions further minimizes the risk of infection and keeps the dog’s surroundings clean and comfortable. In cases of heavy bleeding, gently cleaning the vulva with warm water and a mild, pet-safe cleanser, as advised by a veterinarian, can further enhance hygiene and comfort.
Maintaining proper hygiene during canine estrus offers significant benefits. It reduces the risk of infections, promotes the dog’s comfort, and keeps the home environment clean. Neglecting hygiene can lead to health complications and an unpleasant living situation for both the dog and the owner. Therefore, incorporating hygiene practices into estrus management is a fundamental aspect of responsible dog ownership.
2. Confinement
Confinement is a critical aspect of canine estrus management. Its primary purpose is to prevent mating with male dogs, thus avoiding unwanted pregnancies and contributing to responsible pet population control. Effective confinement strategies also minimize the spread of estrus-related scents that attract males, reducing nuisance behaviors in the neighborhood.
- Indoor Confinement
Keeping the dog indoors during estrus provides a controlled environment where interactions with male dogs can be completely prevented. This requires ensuring all doors and windows are securely closed and that no unsupervised access to the outdoors is possible. For example, even a brief lapse in supervision while a door is open could allow a determined male dog to enter the premises. Indoor confinement also minimizes the spread of estrus-related scents beyond the home.
- Secure Outdoor Confinement
If outdoor access is necessary, a fully enclosed and secure fence is essential. The fence should be high enough to prevent jumping and deep enough to prevent digging underneath. Regularly inspecting the fence for any gaps or weaknesses is crucial. For instance, a small hole under a fence could be exploited by a persistent male dog. Even with a secure fence, direct supervision is recommended during outdoor time to ensure no male dogs are present in neighboring yards.
- Leash Restriction
When walking a dog in estrus, keeping her on a leash at all times is essential, even in typically off-leash areas. This prevents her from roaming and encountering male dogs. Maintaining close control and avoiding areas known to be frequented by other dogs is crucial for successful leash restriction. Even a seemingly friendly interaction could lead to unwanted mating. Therefore, vigilance and proactive avoidance are paramount during leashed walks.
- Social Isolation
During estrus, avoiding dog parks, social gatherings with other dogs, and any situation where the dog might encounter intact males is crucial. Even seemingly brief encounters can result in mating. Therefore, prioritizing isolation from other dogs, particularly males, is a vital aspect of responsible estrus management. This protects the dog and contributes to community-wide efforts to control pet overpopulation. While social interaction is important for dogs, temporary restriction during this period is essential.
These confinement strategies, when implemented diligently and consistently, effectively minimize the risk of unwanted pregnancies during a dog’s estrus cycle. By limiting the dog’s exposure to male dogs and controlling the spread of estrus-related scents, responsible owners contribute to both individual pet well-being and broader animal welfare efforts.
3. Comfort
Comfort plays a significant role in a dog’s well-being during estrus. Physical and emotional changes during this period can cause discomfort and stress. Progesterone fluctuations can lead to mammary gland swelling and tenderness, while hormonal shifts may cause mood swings, resulting in increased anxiety or irritability. A comfortable environment helps mitigate these effects. For example, a dog experiencing discomfort may exhibit restlessness, whining, or changes in appetite. Providing a soft, clean bed in a quiet area can alleviate physical discomfort and promote relaxation. Similarly, offering familiar toys and maintaining consistent routines can reduce anxiety associated with hormonal fluctuations.
Addressing a dog’s comfort needs during estrus involves creating a supportive environment. This includes providing a clean, comfortable resting area away from household commotion. Gentle petting and reassurance can soothe anxiety. Warm compresses, as recommended by a veterinarian, can alleviate discomfort associated with mammary swelling. Avoiding stressful situations, such as interactions with unfamiliar dogs or changes in routine, further promotes a sense of security and well-being. For instance, if a dog exhibits signs of increased clinginess, providing extra attention and reassurance can help her feel more secure. Conversely, if a dog displays irritability, respecting her need for space and avoiding forced interactions can minimize stress.
Prioritizing comfort during estrus contributes significantly to a dog’s overall well-being. Addressing physical discomfort and emotional changes through environmental adjustments and supportive care minimizes stress and promotes a positive experience. Neglecting comfort can exacerbate anxiety and potentially lead to behavioral issues. Therefore, incorporating comfort measures into estrus management demonstrates responsible ownership and strengthens the human-animal bond. Recognizing and responding to a dog’s comfort needs during this time is essential for maintaining her physical and emotional health.
4. Nutrition
Maintaining optimal nutrition during a dog’s estrus cycle is essential for supporting her overall health and well-being. While no specific dietary changes are typically required for healthy dogs, ensuring a balanced and consistent nutritional intake supports the body’s physiological processes during this time. Changes in appetite may occur due to hormonal fluctuations, and addressing these changes through careful dietary management contributes to maintaining stable energy levels and minimizing potential discomfort.
- Consistent Feeding Schedule
Maintaining a regular feeding schedule provides stability during estrus. Hormonal fluctuations can influence appetite, sometimes leading to decreased food intake. Consistency helps regulate the dog’s digestive system and ensures a steady supply of essential nutrients. For example, adhering to a twice-daily feeding schedule, even if the dog consumes slightly less during certain periods of her cycle, helps prevent digestive upset and maintains consistent energy levels.
- High-Quality Diet
Providing a complete and balanced diet formulated for the dog’s life stage is crucial during estrus. This ensures she receives adequate levels of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals necessary for maintaining bodily functions and supporting potential increased energy demands. A high-quality diet contributes to immune system function, which can be particularly important during periods of hormonal fluctuation. For instance, a diet rich in antioxidants can help support the body’s natural defenses.
- Appetite Fluctuations
Appetite changes are common during estrus. Some dogs may experience a decrease in appetite, while others may exhibit an increase. Monitoring food intake and adjusting portion sizes accordingly helps ensure the dog receives adequate nutrition without overfeeding or underfeeding. If significant appetite changes persist, consulting a veterinarian is recommended to rule out any underlying health concerns. For example, if a dog consistently refuses food for more than 24 hours, veterinary advice should be sought.
- Hydration
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial throughout a dog’s estrus cycle. Fresh, clean water should always be available, and encouraging water intake helps support bodily functions and overall health. Monitoring water consumption can also provide insights into the dog’s overall well-being. For example, a sudden increase or decrease in water intake could indicate a potential health issue and warrants veterinary attention.
Nutritional considerations during estrus contribute significantly to a dog’s overall health and well-being. A balanced diet, consistent feeding schedule, and attention to hydration support the body’s physiological processes during this time. Monitoring appetite and seeking veterinary advice when necessary ensures any potential health concerns are addressed promptly. By prioritizing nutrition, owners can help their dogs navigate estrus comfortably and maintain optimal health.
5. Behavior Monitoring
Behavior monitoring is integral to canine estrus management. Hormonal fluctuations during this period influence behavior, often resulting in noticeable changes. These changes can manifest as increased anxiety, irritability, clinginess, restlessness, or even aggression. For example, a normally placid dog might exhibit heightened reactivity to stimuli, while an independent dog might become unusually demanding of attention. Recognizing these shifts is crucial for adapting care strategies and ensuring the dog’s well-being. Failure to monitor behavior can lead to misinterpretations of the dog’s needs and potentially exacerbate stress or create unintended conflicts.
Careful observation provides valuable insights into the dog’s physical and emotional state. Changes in activity levels, sleeping patterns, appetite, and interactions with household members offer clues about her comfort and potential distress. Documenting these changes allows for pattern recognition and informed responses. For instance, increased restlessness and panting could indicate discomfort, prompting the owner to provide a cooler resting area or consult a veterinarian. Similarly, recognizing signs of anxiety, such as excessive licking or pacing, allows for implementing calming strategies like pheromone diffusers or providing a safe, quiet space. This proactive approach minimizes stress and promotes a more comfortable experience for the dog.
Effective behavior monitoring empowers owners to provide individualized care tailored to the dog’s specific needs during estrus. It facilitates early identification of potential health concerns and allows for timely intervention. Understanding behavioral changes within the context of estrus promotes a more empathetic and informed approach to canine care, strengthening the human-animal bond and ensuring the dog’s physical and emotional well-being throughout this natural physiological process. Consistent monitoring, combined with appropriate responses, contributes significantly to a positive estrus experience for both the dog and the owner.
6. Veterinary Consultation
Veterinary consultation plays a crucial role in responsible canine estrus management. While many aspects of estrus care can be managed at home, professional guidance ensures potential health concerns are addressed promptly and comprehensively. Veterinary involvement offers tailored advice based on the individual dog’s breed, age, health history, and specific needs, optimizing care strategies and promoting overall well-being.
- Pre-Estrus Health Evaluation
A pre-estrus veterinary checkup establishes a baseline health assessment. This examination allows the veterinarian to identify any pre-existing conditions that might influence estrus management. For example, a dog with a history of urinary tract infections might require closer monitoring during estrus due to increased risk. This proactive approach allows for tailored preventative measures and facilitates early detection of potential complications.
- Guidance on Hygiene and Confinement
Veterinarians provide expert advice on hygiene practices and confinement strategies specific to the individual dog’s needs and living situation. This guidance ensures optimal sanitation, minimizes the risk of infection, and effectively prevents unwanted mating. For instance, a veterinarian might recommend specific hygiene products based on the dog’s coat type and sensitivity, or suggest tailored confinement strategies for multi-dog households.
- Addressing Behavioral Changes and Discomfort
Veterinary consultation provides valuable insights into managing estrus-related behavioral changes. Professional guidance helps differentiate normal hormonal fluctuations from potential underlying medical issues. For example, if a dog exhibits excessive lethargy or aggression, a veterinarian can determine whether these behaviors are typical estrus manifestations or indicative of a separate health concern requiring specific treatment. They can also recommend strategies for managing discomfort associated with mammary swelling or other physical changes.
- Discussing Long-Term Health Considerations
Veterinary consultation provides an opportunity to discuss long-term health considerations related to estrus, such as spaying or other reproductive health management options. A veterinarian can explain the benefits and risks of different procedures, tailoring recommendations to the individual dog’s circumstances and owner’s preferences. This informed decision-making empowers owners to make choices that align with their dog’s overall health and well-being.
Veterinary consultation provides essential support for navigating canine estrus effectively. Professional guidance complements at-home care, ensuring potential health concerns are addressed proactively and comprehensively. By integrating veterinary expertise into estrus management, owners contribute significantly to their dogs’ health, well-being, and quality of life during this natural physiological process. This proactive approach minimizes potential complications, promotes comfort, and empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog’s reproductive health.
7. Mating Prevention
Mating prevention is a cornerstone of responsible canine estrus management. Preventing unwanted pregnancies safeguards canine welfare, mitigates pet overpopulation, and reduces the strain on animal shelters. During estrus, a female dog is receptive to mating, and without proactive intervention, unintended breeding can readily occur. Therefore, mating prevention strategies are essential for responsible pet ownership.
- Physical Barriers
Physical barriers form the first line of defense against unwanted mating. These include secure confinement indoors or within a fully enclosed outdoor space. Fences must be high enough to prevent jumping and deep enough to prevent digging. Close supervision is necessary even within enclosed areas to ensure no breaches occur. For example, a small gap under a fence could be exploited by a determined male dog. Indoor confinement offers the most secure environment, eliminating the risk of encounters with roaming males. Even seemingly brief unsupervised outdoor access can lead to unintended mating.
- Behavioral Management
Behavioral management techniques complement physical barriers. Avoiding areas frequented by male dogs, such as dog parks or popular walking routes, minimizes the risk of encounters. Keeping the dog on a leash at all times during walks, even in typically off-leash areas, provides crucial control and prevents roaming. For example, encountering a male dog, even on a leash, could lead to unwanted mounting attempts. Therefore, proactive avoidance of such situations is essential.
- Deterrents
Various deterrents can discourage male dogs from approaching a female in estrus. These include commercially available sprays containing pheromones designed to mask the female’s scent. While these products can be helpful, they are not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with other preventative measures. For instance, a strong-smelling deterrent might temporarily discourage a male dog, but it may not be effective long-term or against highly motivated males. Therefore, relying solely on deterrents is not recommended.
- Spaying
Spaying, the surgical removal of the ovaries and uterus, provides a permanent solution to estrus-related challenges, including eliminating the risk of unwanted pregnancies. While not suitable for all dogs or situations, it offers a long-term solution for owners not intending to breed their female dogs. Spaying eliminates estrus cycles entirely, thereby preventing the associated behavioral changes and the need for ongoing mating prevention strategies. It also offers significant health benefits, including reducing the risk of certain cancers and uterine infections.
Integrating these mating prevention strategies into a comprehensive estrus management plan ensures responsible pet ownership. Preventing unwanted pregnancies contributes to community-wide animal welfare efforts and safeguards individual dog well-being. By combining physical barriers, behavioral management techniques, deterrents, and considering long-term options like spaying, owners can effectively navigate the challenges of canine estrus and promote responsible pet population control.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding canine estrus care, providing concise and informative responses to promote understanding and responsible pet ownership.
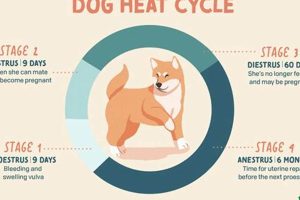
Question 1: How long does a dog’s estrus cycle typically last?
Estrus typically lasts between 2 to 4 weeks, although variations can occur depending on breed and individual factors.
Question 2: How frequently do dogs experience estrus?
Most dogs experience estrus approximately every six months, although this frequency can vary, particularly in younger or older dogs.
Question 3: What are the primary signs of estrus in dogs?
Key indicators include swelling of the vulva, bloody discharge, increased urination, behavioral changes such as restlessness or clinginess, and attraction of male dogs.
Question 4: Can a dog become pregnant during her first estrus cycle?
Yes, pregnancy is possible during a dog’s first estrus. Therefore, implementing preventative measures from the onset of the first cycle is crucial.
Question 5: What are the most effective methods for preventing mating during estrus?
Effective strategies include strict confinement indoors or in a secure outdoor area, avoiding contact with male dogs, using deterrents, and considering spaying as a long-term solution.
Question 6: When should veterinary consultation be sought regarding estrus?
Veterinary guidance is recommended if unusual or concerning symptoms arise, such as prolonged or excessively heavy bleeding, behavioral changes indicative of distress, or if mating prevention strategies are unsuccessful.
Understanding the nuances of canine estrus empowers owners to provide appropriate care and make informed decisions regarding their dog’s reproductive health. Consulting a veterinarian for personalized advice is always recommended.
The following section will offer further resources and support for navigating canine estrus effectively.
Conclusion
Managing a dog’s estrus cycle requires a multifaceted approach encompassing hygiene, confinement, comfort, nutrition, behavior monitoring, and veterinary consultation. Preventing unwanted pregnancies remains paramount, necessitating diligent implementation of appropriate strategies. Understanding the physiological and behavioral changes associated with estrus equips owners to provide optimal care and support.
Responsible estrus management contributes significantly to canine welfare and responsible pet ownership. Prioritizing a dog’s physical and emotional needs during this time strengthens the human-animal bond and promotes a positive, healthy experience. Continued education and proactive veterinary engagement empower owners to navigate the complexities of canine estrus effectively, ensuring optimal well-being for their companions.