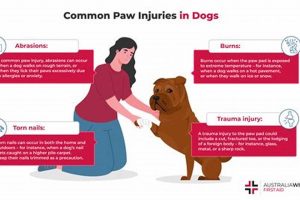
Canine care encompasses a range of responsibilities crucial for a dog’s physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. This includes providing for basic needs like nutritious food, fresh water, safe shelter, and regular exercise. It also extends to preventative healthcare, such as vaccinations and parasite control, and addressing behavioral needs through training and socialization.
Proper canine guardianship yields significant benefits. Healthy dogs experience greater longevity, enhanced vitality, and a reduced risk of developing serious medical conditions. Furthermore, a well-cared-for dog typically exhibits fewer behavioral problems, contributing to a more harmonious household and stronger bond between animal and owner. Historically, the human-canine relationship has evolved from working partnerships to close companionship, underscoring the ethical responsibility to provide optimal care.
The following sections will explore the core components of responsible dog ownership, offering practical guidance on nutrition, exercise, health management, training, and creating a safe and enriching environment.
Essential Canine Care Tips
Providing optimal canine care involves consistent attention to several key areas. These tips offer guidance on responsible dog ownership practices.
Tip 1: Nutritional Needs: A balanced diet is fundamental to canine health. Select high-quality dog food appropriate for the animal’s age, breed, and activity level. Consult a veterinarian for guidance on dietary requirements and portion control.
Tip 2: Exercise and Enrichment: Regular physical activity and mental stimulation are vital. Provide opportunities for daily walks, playtime, and interactive games to prevent boredom and promote physical and mental well-being.
Tip 3: Preventative Healthcare: Vaccinations, parasite prevention, and routine veterinary checkups are crucial for disease prevention and early detection of health issues. Adherence to a preventative healthcare schedule is essential.
Tip 4: Training and Socialization: Early training and socialization are key to developing a well-behaved and well-adjusted dog. Consistent positive reinforcement methods are recommended.
Tip 5: Safe and Comfortable Environment: Provide a safe, clean, and comfortable living environment. Ensure access to fresh water, appropriate shelter, and a dedicated resting area.
Tip 6: Dental Hygiene: Regular dental care helps prevent dental disease. Brush a dog’s teeth regularly using veterinarian-approved toothpaste and provide appropriate chew toys.
Tip 7: Grooming: Regular grooming, including brushing and bathing, helps maintain a healthy coat and skin. Frequency depends on breed and coat type.
Consistent application of these tips contributes significantly to a dog’s overall health, happiness, and longevity. These practices foster a strong bond between dog and owner.
By understanding and addressing these key aspects of canine care, one can ensure a fulfilling and enriching life for their canine companion.
1. Nutrition
Proper nutrition forms the cornerstone of canine health and well-being, directly impacting a dog’s lifespan, energy levels, and overall quality of life. Understanding canine nutritional requirements is essential for responsible ownership and forms a critical component of comprehensive dog care.
- Dietary Requirements:
Canines require a balanced diet consisting of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Protein provides essential amino acids for muscle development and tissue repair. Fats provide energy and support healthy skin and coat. Carbohydrates offer a readily available energy source. Vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in various bodily functions. The specific proportions of these nutrients vary based on a dog’s age, breed, activity level, and health status.
- Commercial Dog Food:
Commercially available dog foods offer a convenient way to provide complete and balanced nutrition. Dry kibble, wet food, and raw diets are common options. Selecting a high-quality dog food that meets Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) standards ensures it contains the necessary nutrients. Reading and understanding pet food labels is crucial for making informed choices.
- Homemade Diets:
Some owners opt to prepare homemade dog food. While offering potential benefits like ingredient control, formulating a balanced homemade diet requires careful planning and consultation with a veterinary nutritionist. Nutritional deficiencies or excesses can have serious health implications, making professional guidance essential.
- Feeding Practices:
Establishing healthy feeding practices is vital. Feeding schedules, portion control, and avoiding table scraps contribute to weight management and prevent digestive issues. Fresh water should always be readily available. Monitoring a dog’s weight and adjusting food intake as needed helps maintain optimal body condition.
By understanding and addressing these key nutritional facets, owners can contribute significantly to their dog’s overall health, longevity, and quality of life. Nutritional care is an integral part of responsible dog ownership, directly impacting a dog’s physical condition, behavior, and ability to thrive.
2. Exercise
Physical activity is a cornerstone of canine well-being, impacting not only physical health but also mental and behavioral health. Adequate exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, preventing obesity-related health issues, and promoting proper musculoskeletal development. Furthermore, it serves as an outlet for pent-up energy, reducing the likelihood of destructive behaviors stemming from boredom or frustration. A structured exercise regimen contributes significantly to a dog’s overall quality of life and reinforces the human-animal bond.
- Types of Exercise:
Canine exercise encompasses various activities, each catering to different needs and preferences. Daily walks provide essential physical and mental stimulation, allowing dogs to explore their environment and engage their senses. Running, hiking, and swimming offer more vigorous exercise options for energetic breeds. Playtime with interactive toys, such as fetch or tug-of-war, provides both physical and mental engagement. The choice of activity should align with a dog’s breed, age, and health status.
- Frequency and Duration:
The appropriate frequency and duration of exercise vary depending on individual factors such as breed, age, and energy level. Most dogs benefit from at least one to two walks per day, totaling 30 minutes to an hour of exercise. Highly active breeds may require more extensive exercise routines. Monitoring a dog’s behavior and adjusting exercise accordingly helps ensure their needs are met.
- Benefits of Exercise:
The benefits of regular exercise extend beyond physical health. Exercise aids in weight management, strengthens cardiovascular health, and improves muscle tone. It also provides mental stimulation, reduces stress and anxiety, and promotes better sleep. A well-exercised dog is typically more content, less prone to behavioral problems, and easier to train.
- Safety Considerations:
Ensuring safe exercise practices is crucial. Using appropriate leashes, harnesses, and collars prevents escapes and injuries. Avoiding extreme temperatures and providing access to water during exercise prevents heatstroke and dehydration. Being mindful of a dog’s physical limitations and avoiding overexertion safeguards their well-being. Gradual increases in exercise intensity prevent injuries, especially in puppies and older dogs.
Integrating regular exercise into a dog’s routine is paramount for their overall health and well-being. A balanced exercise program contributes significantly to a happier, healthier, and more well-adjusted canine companion, strengthening the bond between dog and owner and enhancing the quality of life for both. Neglecting a dog’s exercise needs can lead to behavioral problems, health issues, and a diminished quality of life.
3. Healthcare
Preventative healthcare forms a critical pillar of responsible dog ownership, directly impacting a dog’s long-term health, well-being, and quality of life. Proactive healthcare measures not only prevent diseases and mitigate potential health risks but also contribute to early detection and treatment of medical conditions, ultimately promoting a longer, healthier lifespan. Implementing a comprehensive healthcare plan is an essential aspect of providing optimal canine care.
- Vaccinations:
Vaccinations protect dogs from various infectious diseases, some of which can be life-threatening. Core vaccines, considered essential for all dogs, protect against distemper, parvovirus, adenovirus, and rabies. Non-core vaccines, recommended based on individual risk factors, offer protection against diseases like Lyme disease, leptospirosis, and kennel cough. Adhering to a veterinarian-recommended vaccination schedule is crucial for establishing and maintaining immunity.
- Parasite Control:
Parasites, both internal and external, pose significant health risks to canines. Fleas, ticks, heartworms, intestinal worms, and other parasites can cause a range of health problems, from skin irritation to life-threatening organ damage. Preventative measures, such as monthly flea and tick preventatives and heartworm medication, are essential for protecting dogs from parasitic infestations. Regular fecal examinations aid in early detection and treatment of intestinal parasites.
- Veterinary Checkups:
Routine veterinary checkups play a vital role in maintaining canine health. Regular examinations allow veterinarians to monitor a dog’s overall health, detect potential problems early, and provide preventative care guidance. Annual checkups are typically recommended for healthy adult dogs, while senior dogs and those with pre-existing conditions may require more frequent visits. These checkups provide opportunities for vaccinations, parasite control, dental care, and addressing any emerging health concerns.
- Dental Care:
Dental health is an often overlooked but critical aspect of canine healthcare. Periodontal disease, a common ailment in dogs, can lead to pain, tooth loss, and systemic health issues. Regular dental care, including brushing a dog’s teeth with veterinarian-approved toothpaste and providing dental chews, helps prevent plaque buildup and maintain oral hygiene. Professional dental cleanings, performed under anesthesia by a veterinarian, are recommended as needed to remove tartar and address existing dental problems.
By prioritizing these healthcare components, owners can significantly reduce the risk of disease, enhance their dog’s overall well-being, and foster a longer, healthier life. Integrating preventative healthcare measures into a dog’s routine demonstrates a commitment to responsible ownership and reinforces the importance of proactive care in maintaining optimal canine health. Neglecting preventative healthcare can lead to preventable illnesses, compromised quality of life, and potentially higher veterinary costs in the long run.
4. Training
Effective training is an integral component of responsible dog ownership, directly influencing a dog’s behavior, well-being, and integration into human society. It establishes clear communication between dog and owner, fostering a harmonious relationship built on mutual understanding and respect. Consistent training promotes desirable behaviors, mitigates undesirable ones, and enhances a dog’s ability to navigate various social situations and environmental stimuli. A well-trained dog experiences reduced stress and anxiety, contributing to improved overall well-being and a stronger bond with its owner.
- Basic Obedience:
Basic obedience training forms the foundation for all other training endeavors. It involves teaching fundamental commands such as sit, stay, come, down, and heel. These commands provide essential control and structure, enabling owners to manage their dogs effectively in various situations. Basic obedience training enhances safety, facilitates socialization, and establishes a framework for clear communication between dog and owner.
- Socialization:
Early socialization plays a crucial role in shaping a dog’s behavior and temperament. Exposing puppies to various people, places, sounds, and experiences during their critical developmental period helps them develop into well-adjusted, confident adults. Proper socialization mitigates fear and aggression, enabling dogs to interact appropriately with other dogs, humans, and novel stimuli. It equips dogs with the social skills necessary to thrive in diverse environments and fosters positive interactions.
- House Training:
House training, or housebreaking, teaches dogs appropriate elimination habits. It involves establishing a consistent routine, rewarding desired behaviors, and addressing accidents calmly and consistently. Successful house training contributes to a clean and hygienic home environment and reduces stress for both dog and owner. Crate training can be a valuable tool in house training, providing a designated den-like space and aiding in establishing a predictable elimination schedule.
- Behavioral Modification:
Behavioral modification techniques address specific problem behaviors such as excessive barking, chewing, digging, or aggression. These techniques typically involve identifying the underlying causes of the behavior, implementing strategies to modify the behavior, and consistently reinforcing desired responses. Behavioral modification may involve professional guidance from a certified dog trainer or veterinary behaviorist, particularly for complex or deeply ingrained behavioral issues.
Integrating these facets of training into a dog’s life contributes significantly to a well-behaved, well-adjusted, and happy companion. Consistent training enhances the human-animal bond, promoting a stronger, more fulfilling relationship built on mutual trust and understanding. Furthermore, effective training ensures a dog’s safety and well-being, enabling it to navigate the human world with confidence and ease. A well-trained dog is a joy to own, enriching the lives of both the dog and its human companions.
5. Environment
A dog’s environment significantly influences its physical and psychological well-being. A safe, comfortable, and enriching environment is crucial for promoting healthy development, reducing stress, and fostering a positive human-animal bond. Several environmental factors contribute to a dog’s overall quality of life. Providing appropriate shelter protects dogs from harsh weather conditions and provides a sense of security. Access to fresh water is essential for hydration and overall health. A dedicated resting area allows dogs to relax and de-stress. A stimulating environment, incorporating toys, puzzles, and opportunities for exploration, prevents boredom and promotes mental engagement. For example, a dog living in a cramped, unsanitary space with limited access to fresh water and exercise opportunities is likely to experience stress, potentially leading to behavioral problems and health issues. Conversely, a dog living in a spacious, clean environment with access to enrichment activities and a comfortable resting area is more likely to exhibit balanced behavior and thrive.
Creating an environment that caters to a dog’s specific needs requires careful consideration of several factors. Breed-specific needs influence environmental requirements. For instance, a large, energetic breed requires more space and opportunities for exercise than a small, less active breed. Age also plays a role. Puppies require a safe environment free from hazards, while senior dogs may benefit from orthopedic bedding and easier access to resources. Individual temperaments and health conditions further dictate environmental modifications. An anxious dog may benefit from a quiet, secure den-like space, while a dog with mobility issues requires ramps or other assistive devices. Practical applications include providing appropriate bedding, ensuring adequate ventilation and temperature control, minimizing exposure to loud noises and stressful stimuli, and offering opportunities for social interaction and environmental exploration.
A well-designed environment is fundamental to responsible dog ownership. Addressing a dog’s environmental needs contributes significantly to its physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Failing to provide a suitable environment can negatively impact a dog’s behavior, health, and development. Understanding the profound impact of environment allows owners to create spaces that foster contentment, promote well-being, and strengthen the human-animal bond, contributing to a harmonious and fulfilling relationship between dog and owner. This understanding underpins responsible dog ownership and promotes a positive, enriching life for canine companions.
6. Grooming
Regular grooming constitutes a vital aspect of canine care, significantly impacting a dog’s health, hygiene, and overall well-being. Beyond enhancing a dog’s appearance, grooming serves essential functions in maintaining skin and coat health, preventing matting and infections, and providing opportunities for early detection of potential health issues. Integrating routine grooming practices into a dog’s care regimen demonstrates responsible ownership and contributes to a stronger human-animal bond.
- Brushing:
Regular brushing removes loose hair and dead skin cells, preventing matting and promoting healthy coat growth. The frequency of brushing varies depending on coat type and length. Breeds with long, dense coats require daily brushing to prevent tangles and mats, while short-haired breeds may only require weekly brushing. Brushing also distributes natural oils, promoting a healthy sheen and preventing skin dryness. This process provides an opportunity to inspect the skin for parasites, lumps, or other abnormalities.
- Bathing:
Bathing removes dirt, debris, and excess oils, keeping a dog clean and odor-free. The frequency of bathing depends on breed, lifestyle, and individual needs. Over-bathing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Using a dog-specific shampoo and conditioner helps maintain skin and coat health. Thorough drying after bathing is essential to prevent chilling and skin infections.
- Nail Trimming:
Regular nail trimming prevents overgrowth, which can lead to discomfort, difficulty walking, and potential skeletal problems. Overgrown nails can also curl inwards, piercing the paw pads and causing pain and infection. Using appropriate nail clippers and employing proper techniques prevents injury to the quick. For dogs unaccustomed to nail trimming, gradual desensitization and positive reinforcement techniques can ease the process.
- Ear Cleaning:
Regular ear cleaning helps prevent ear infections, a common ailment in dogs. Excessive wax buildup and debris create a breeding ground for bacteria and yeast. Using a veterinarian-approved ear cleaning solution and gentle techniques removes wax and debris without causing irritation. Inspecting the ears regularly for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, allows for prompt veterinary intervention if needed.
These interconnected grooming practices contribute significantly to a dog’s overall health and well-being. By incorporating these practices into a regular care routine, owners demonstrate a commitment to responsible canine guardianship. Consistent grooming not only maintains a dog’s physical health but also strengthens the human-animal bond through regular close interaction and tactile stimulation. Neglecting grooming can lead to various health issues, behavioral problems, and a diminished quality of life for the dog. Therefore, understanding and addressing grooming needs forms an essential part of providing comprehensive canine care.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dog Care
This section addresses common queries regarding canine care, providing concise and informative responses to facilitate informed decision-making and responsible pet ownership.
Question 1: How often should a dog be fed?
Feeding frequency depends on a dog’s age, breed, activity level, and individual dietary needs. Adult dogs typically thrive on one to two meals per day, while puppies require more frequent feedings. Consulting a veterinarian can provide tailored guidance.
Question 2: What constitutes a balanced canine diet?
A balanced diet provides essential nutrients, including proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, in appropriate proportions. High-quality commercial dog food formulated to meet AAFCO standards generally fulfills these requirements. Homemade diets require careful planning and veterinary consultation.
Question 3: How much exercise does a dog need?
Exercise requirements vary based on breed, age, and energy level. Most dogs benefit from at least 30 minutes to an hour of exercise daily, which can include walks, playtime, and other activities. Consulting a veterinarian can help determine appropriate exercise regimens.
Question 4: How often should a dog be groomed?
Grooming frequency depends on coat type and length. Regular brushing, bathing, nail trimming, and ear cleaning are essential components of canine hygiene. Breeds with long coats require more frequent brushing to prevent matting, while all dogs benefit from regular nail trims and ear cleaning.
Question 5: When should a dog be taken to the veterinarian?
Annual veterinary checkups are recommended for healthy adult dogs, while puppies and senior dogs may require more frequent visits. Additionally, any signs of illness, injury, or behavioral changes warrant prompt veterinary attention.
Question 6: How can one prevent behavioral problems in dogs?
Early socialization, consistent training using positive reinforcement methods, and providing a stimulating and enriching environment are key to preventing behavioral problems. Addressing underlying anxieties or fears through appropriate training and environmental modifications can also mitigate behavioral issues.
Consistent application of these principles contributes significantly to a dog’s overall health and well-being. Consultation with a veterinarian or certified professional remains essential for addressing individual needs and concerns.
For further information on specific breeds and individual needs, consult reputable resources such as the American Kennel Club (AKC) or the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA).
Conclusion
Comprehensive canine care encompasses a multifaceted approach, addressing crucial aspects of a dog’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being. From providing balanced nutrition and adequate exercise to ensuring preventative healthcare and fostering a stimulating environment, responsible guardianship requires diligent attention to detail and a commitment to meeting a dog’s evolving needs. Effective training and consistent grooming further contribute to a dog’s overall health and happiness, strengthening the human-animal bond and enriching the lives of both dog and owner. Understanding and implementing these core tenets of canine care are fundamental to responsible pet ownership.
Ultimately, providing optimal care for a canine companion represents a significant responsibility, one that yields immeasurable rewards. A well-cared-for dog thrives, experiencing enhanced physical health, improved behavioral balance, and a deeper connection with its human family. Prioritizing a dog’s well-being not only ensures a fulfilling life for the animal but also fosters a more harmonious and enriching coexistence between humans and their canine companions. This commitment to responsible care benefits individual animals and contributes to a more compassionate and humane society.