Providing for a canine companion encompasses various responsibilities, including meeting their physical, emotional, and social needs. This involves providing nutritious food, fresh water, regular exercise, a safe and comfortable environment, and preventative healthcare such as vaccinations and parasite control. For example, a balanced diet specifically formulated for a dog’s age and breed is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing dietary deficiencies. Regular veterinary checkups are equally crucial for early disease detection and ensuring a long, healthy life.
Proper canine husbandry contributes significantly to an animal’s well-being and strengthens the human-animal bond. A well-cared-for dog is more likely to be happy, healthy, and well-behaved. Historically, dogs have served various roles, from working partners to loyal companions, and their welfare has always been linked to their ability to perform these roles effectively. Modern approaches emphasize the importance of understanding canine behavior and providing enrichment activities that stimulate their minds and bodies. This can involve interactive play, training, and socialization with other dogs and people.
The following sections delve into specific aspects of responsible canine guardianship, offering practical guidance and expert advice on nutrition, exercise, training, healthcare, and creating a nurturing environment. These topics provide a comprehensive framework for ensuring the well-being of canine companions and fostering a strong, fulfilling relationship between humans and their dogs.
Essential Canine Care Tips
Providing optimal care for a canine companion requires attention to several key areas. The following tips offer practical guidance for ensuring a dog’s physical and emotional well-being.
Tip 1: Nutritional Needs: A balanced diet tailored to a dog’s age, breed, and activity level is crucial. High-quality commercial dog food, or a carefully prepared homemade diet under veterinary supervision, should be provided. Fresh water should always be available.
Tip 2: Exercise and Enrichment: Regular physical activity and mental stimulation are vital for a dog’s health and happiness. Daily walks, playtime, and engaging toys can prevent boredom and behavioral issues.
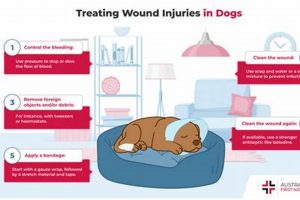
Tip 3: Veterinary Care: Preventative healthcare, including vaccinations, parasite control, and regular checkups, is essential for early disease detection and maintaining overall health.
Tip 4: Safe Environment: A secure and comfortable living space, free from hazards, is paramount. This includes a comfortable resting area, protection from extreme weather, and a safe, fenced yard.
Tip 5: Training and Socialization: Basic obedience training and socialization with other dogs and people are crucial for developing good behavior and adaptability.
Tip 6: Grooming and Hygiene: Regular grooming, including brushing, bathing, and nail trimming, contributes to a dog’s overall health and comfort.
Tip 7: Dental Care: Maintaining good oral hygiene through regular teeth brushing or dental chews helps prevent dental disease and promotes overall health.
Tip 8: Observation and Attention: Regularly monitoring a dog’s behavior, appetite, and elimination habits allows for early detection of potential health problems.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes a long, healthy, and fulfilling life for canine companions and strengthens the bond between humans and their dogs.
By understanding and addressing these crucial aspects of canine care, one can ensure a positive and enriching experience for both the dog and the owner. This foundation of care creates a harmonious relationship built on mutual respect, trust, and well-being.
1. Nutrition
Optimal canine health and well-being rely heavily on proper nutrition. A balanced diet provides the essential nutrients necessary for growth, development, and overall vitality. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to various health issues, impacting a dog’s physical condition, behavior, and lifespan. Understanding and meeting a dog’s nutritional requirements is a cornerstone of responsible canine guardianship.
- Macronutrient Balance:
Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are the building blocks of a dog’s diet. Proteins provide amino acids for muscle growth and repair. Fats provide energy and support healthy skin and coat. Carbohydrates offer a readily available energy source. The correct balance of these macronutrients is crucial for maintaining optimal body condition and supporting various bodily functions. For example, a growing puppy requires a higher protein intake than an adult dog. Dietary imbalances can lead to obesity, malnutrition, or other health complications.
- Micronutrient Requirements:
Vitamins and minerals, while needed in smaller amounts, play vital roles in various physiological processes. These micronutrients support immune function, bone health, and overall metabolic function. Calcium, for example, is crucial for bone development, while vitamin D aids in calcium absorption. A deficiency in essential vitamins or minerals can lead to specific health problems, such as anemia or weakened bones.
- Hydration:
Access to fresh, clean water is paramount for maintaining proper hydration. Water plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and removing waste products. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, particularly during periods of increased activity or hot weather.
- Dietary Considerations:
Specific dietary requirements vary depending on factors such as breed, age, activity level, and underlying health conditions. Large breed puppies, for instance, have different nutritional needs than small breed adults. Dogs with allergies or specific medical conditions may require specialized diets formulated to address their individual needs. Consulting a veterinarian can provide tailored guidance for selecting an appropriate diet.
By addressing these key nutritional facets, responsible owners can contribute significantly to their canine companions’ long-term health and well-being. Proper nutrition forms the foundation for a healthy life, supporting growth, activity, and overall vitality. A balanced diet, tailored to individual needs, is an investment in a dog’s long-term health and happiness.
2. Environment
A dog’s environment significantly impacts its physical and psychological well-being. Providing a safe, comfortable, and stimulating environment is crucial for promoting healthy development, reducing stress, and preventing behavioral issues. A suitable environment encompasses several key factors, including physical space, sensory stimulation, and social interaction. For instance, a dog confined to a small, barren space without opportunities for exercise or exploration may develop anxiety, destructive behaviors, or depression. Conversely, a dog provided with ample space, engaging toys, and regular social interaction is more likely to exhibit balanced behavior and thrive.
Several environmental factors contribute to a dog’s overall welfare. Adequate space allows for natural movement and exploration. A comfortable resting area provides a sense of security and promotes relaxation. Protection from extreme weather conditions, such as excessive heat or cold, safeguards against health risks. Access to fresh air and natural light contributes to physical and mental well-being. Enrichment activities, such as puzzle toys or interactive games, provide mental stimulation and prevent boredom. A clean and hygienic environment reduces the risk of infections and promotes overall health. Considering these elements contributes significantly to creating a supportive and nurturing space for a canine companion.
Creating an optimal environment requires careful consideration of a dog’s specific needs and breed characteristics. Some breeds thrive in active, outdoor environments with ample space to run and explore, while others are better suited to calmer, indoor settings. Understanding these breed-specific needs allows owners to tailor the environment accordingly. Providing a well-structured environment that caters to a dog’s physical and emotional needs is an investment in their overall well-being and promotes a strong, positive human-animal bond. Neglecting environmental factors can lead to behavioral problems, health issues, and a diminished quality of life. Prioritizing environmental enrichment demonstrates a commitment to responsible canine guardianship and contributes significantly to a dogs long-term happiness and health.
3. Health
Canine health represents a cornerstone of responsible animal guardianship. A proactive approach to health maintenance directly influences a dog’s quality of life, impacting longevity, vitality, and overall well-being. This encompasses preventative measures, prompt veterinary attention when needed, and an ongoing awareness of potential health risks. Neglecting health considerations can lead to preventable suffering, diminished quality of life, and potentially shortened lifespans. For instance, routine vaccinations protect against infectious diseases like parvovirus and distemper, which can be life-threatening, particularly in puppies. Regular dental care prevents periodontal disease, a common ailment that can lead to pain, tooth loss, and even systemic infections. Similarly, parasite prevention protects against heartworm, fleas, and ticks, which can transmit diseases and cause significant discomfort.
Maintaining optimal canine health requires a multifaceted approach. Regular veterinary checkups facilitate early disease detection and allow for timely intervention. These checkups typically include physical examinations, vaccinations, and parasite prevention. A veterinarian can also provide guidance on breed-specific health predispositions and recommend appropriate screening tests. For example, certain breeds are prone to hip dysplasia, a condition that can cause pain and mobility issues. Early detection through regular screenings allows for proactive management and can significantly improve a dog’s long-term prognosis. Furthermore, attentive observation by owners plays a crucial role in identifying potential health problems. Changes in appetite, behavior, or elimination habits can indicate underlying health issues and warrant veterinary consultation. Promptly addressing these signs can prevent minor issues from escalating into more serious and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Prioritizing canine health requires consistent effort and a proactive mindset. Understanding breed-specific health risks, adhering to preventative health protocols, and seeking prompt veterinary attention when necessary are essential components of responsible canine guardianship. This proactive approach not only mitigates potential health risks but also strengthens the human-animal bond, fostering a relationship built on trust, care, and a shared commitment to well-being. Failing to prioritize health can lead to significant challenges, both for the dog and the owner, impacting finances, emotional well-being, and the overall quality of the human-animal relationship. Investing in canine health translates to a richer, more fulfilling companionship and contributes to a longer, healthier, and happier life for the animal.
4. Exercise
Canine exercise is integral to responsible care, significantly influencing physical and mental well-being. Adequate physical activity contributes to maintaining a healthy weight, preventing obesity-related health issues, and promoting cardiovascular health. Furthermore, exercise provides essential mental stimulation, reducing boredom, anxiety, and the potential for destructive behaviors. A lack of sufficient exercise can lead to various health problems, including obesity, joint issues, and behavioral problems such as excessive barking, chewing, and digging.
- Physical Health Benefits:
Regular exercise strengthens muscles, improves cardiovascular function, and helps maintain a healthy weight. Activities like walking, running, and swimming contribute to overall physical fitness and reduce the risk of developing obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. For example, daily walks provide necessary physical activity while also allowing dogs to explore their environment and engage their senses.
- Mental Stimulation:
Exercise offers crucial mental stimulation, preventing boredom and reducing the likelihood of destructive behaviors stemming from pent-up energy or frustration. Activities like fetch, playing with interactive toys, and navigating obstacle courses engage a dog’s mind and provide outlets for natural instincts. This mental engagement contributes to a balanced temperament and reduces the risk of anxiety and depression. For instance, puzzle toys that dispense treats challenge a dog’s problem-solving skills and provide a rewarding form of mental exercise.
- Behavioral Benefits:
Sufficient exercise can significantly improve behavior by providing an outlet for excess energy and reducing frustration. Dogs who receive adequate exercise are less likely to exhibit destructive behaviors such as excessive barking, chewing, or digging. Regular physical activity also promotes better sleep patterns and reduces restlessness. Structured exercise, such as obedience training combined with physical activity, can further enhance focus and improve responsiveness to commands. For example, a dog who regularly engages in fetch is more likely to be calm and well-behaved indoors.
- Socialization Opportunities:
Exercise often provides opportunities for socialization, which is crucial for developing appropriate social skills and reducing fear or aggression towards other dogs or people. Dog parks, group walks, and playdates with other dogs provide valuable social interaction. These experiences help dogs learn appropriate social cues and develop confidence in various social settings. Positive social interactions contribute to a well-adjusted temperament and reduce the risk of social anxiety or reactivity. For example, regular visits to a dog park can help a shy dog become more comfortable and confident around other dogs.
These interconnected facets of exercise underscore its importance in comprehensive canine care. By prioritizing exercise, owners contribute significantly to their dogs’ physical health, mental well-being, and behavioral balance. A well-exercised dog is more likely to be a healthy, happy, and well-adjusted companion, strengthening the human-animal bond and enriching the lives of both dog and owner. Neglecting exercise can have detrimental effects, leading to various health and behavioral problems that compromise a dog’s overall well-being and quality of life. Incorporating regular, appropriate exercise into a dog’s routine is a fundamental aspect of responsible canine guardianship.
5. Socialization
Socialization is a critical component of comprehensive canine care, directly influencing a dog’s behavioral development, emotional well-being, and ability to navigate the world confidently. Proper socialization involves exposing a dog to a variety of people, animals, environments, and experiences during key developmental periods, shaping their responses and reducing the likelihood of fear, anxiety, or aggression in later life. Neglecting socialization can result in behavioral challenges, impacting a dog’s quality of life and its relationship with its human companions. A well-socialized dog is more likely to be adaptable, confident, and well-adjusted, enriching the lives of both the dog and its owner.
- Early Exposure:
The most crucial socialization period occurs during puppyhood, typically between 3 and 14 weeks of age. During this time, puppies are highly receptive to new experiences and form lasting impressions. Exposure to various sights, sounds, smells, and textures during this period helps them develop positive associations and adapt to different environments. For example, introducing a puppy to different surfaces like grass, carpet, and tile helps them become comfortable with various textures underfoot. Early exposure to friendly, vaccinated dogs and people of different ages, genders, and appearances is essential for developing appropriate social skills and reducing the risk of fear-based aggression later in life. Missing this critical window can make it more challenging to address behavioral issues later on.
- Continued Socialization:
While early puppyhood is crucial, socialization is an ongoing process that should continue throughout a dog’s life. Regular exposure to novel situations, people, and animals helps maintain their adaptability and prevents the development of fear or anxiety. This continued socialization can involve enrolling in obedience classes, visiting dog parks, participating in group walks, or simply encountering new people and dogs during regular walks. Consistent exposure to varied stimuli reinforces positive associations and helps dogs maintain their social skills. For instance, regularly taking a dog to new locations, such as parks, hiking trails, or pet-friendly stores, helps them become comfortable in different environments and reduces the likelihood of reactivity.
- Positive Reinforcement:
Positive reinforcement techniques are essential during socialization. Creating positive associations with new experiences helps build confidence and reduces fear or anxiety. Rewarding calm and appropriate behavior with treats, praise, or toys reinforces positive interactions. For example, when introducing a puppy to a new person, rewarding calm behavior helps create a positive association with meeting strangers. Conversely, punishing a dog for displaying fear or anxiety can exacerbate the problem and create negative associations. Using positive reinforcement methods ensures that socialization experiences are enjoyable and contribute to a dog’s emotional well-being.
- Recognizing and Addressing Fear or Anxiety:
Observing a dog’s body language during socialization is crucial for recognizing signs of fear or anxiety. Signs such as tucked tails, flattened ears, lip licking, yawning, or avoidance behavior indicate discomfort. If a dog exhibits these signs, it’s important to remove them from the situation and create a safe, comfortable space. Forcing a fearful dog into a stressful situation can worsen their anxiety and create negative associations. Consulting with a certified professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide valuable guidance on addressing fear or anxiety and developing a tailored socialization plan.
These interconnected facets of socialization highlight its crucial role in overall canine care. Proper socialization contributes significantly to a dog’s behavioral development, emotional well-being, and ability to thrive in various social settings. A well-socialized dog is more likely to be a confident, adaptable, and well-adjusted companion, strengthening the human-animal bond and enriching the lives of both the dog and its owner. By prioritizing socialization as an integral component of care, owners invest in their dog’s long-term well-being and contribute to a harmonious and fulfilling relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Care
This section addresses common inquiries regarding canine care, offering practical insights and guidance for responsible pet ownership.
Question 1: How often should a dog be fed?
Feeding frequency depends on a dog’s age, breed, activity level, and individual dietary needs. Puppies generally require more frequent meals than adult dogs. Consulting a veterinarian can provide tailored feeding recommendations.
Question 2: What constitutes a balanced canine diet?
A balanced canine diet provides the essential nutrients required for optimal health and well-being. This includes appropriate levels of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Commercial dog foods formulated for specific life stages and breeds often provide a balanced nutritional profile. Homemade diets should be carefully formulated under veterinary supervision to ensure nutritional adequacy.
Question 3: How much exercise does a dog require?
Exercise requirements vary depending on breed, age, and overall health. Most dogs benefit from daily walks, playtime, and opportunities for mental stimulation. Consulting a veterinarian can help determine appropriate exercise levels based on individual needs.
Question 4: When should veterinary care be sought?
Veterinary care should be sought for routine checkups, vaccinations, and parasite prevention. Additionally, any signs of illness, injury, or behavioral changes warrant prompt veterinary attention. Early intervention can often prevent minor health issues from escalating into more serious conditions.
Question 5: How can destructive chewing be addressed?
Destructive chewing can often be addressed by providing appropriate chew toys, ensuring sufficient exercise and mental stimulation, and implementing consistent training techniques. Identifying and addressing underlying causes, such as anxiety or boredom, is crucial for effectively managing this behavior.
Question 6: What are the key signs of a healthy dog?
Key indicators of canine health include a healthy appetite, consistent energy levels, a shiny coat, clear eyes, healthy gums, and regular bowel movements. Regular veterinary checkups are essential for confirming overall health and addressing any potential concerns.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of canine care contributes to responsible pet ownership and promotes a long, healthy, and fulfilling life for canine companions. Consistent attention to these factors strengthens the human-animal bond and enhances the overall quality of the relationship.
For further information on specific aspects of canine care, please consult the subsequent sections or seek professional guidance from a veterinarian or certified dog trainer.
Conclusion
Providing comprehensive and attentive care for canine companions is a significant responsibility. This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted nature of proper canine husbandry, encompassing crucial elements such as nutrition, environment, health, exercise, and socialization. Each of these facets contributes significantly to a dog’s overall well-being, influencing physical health, emotional balance, and behavioral development. Understanding and addressing these interconnected needs is fundamental to responsible pet ownership.
Ultimately, committed canine care fosters a strong human-animal bond, enriching the lives of both dog and owner. Prioritizing a dog’s well-being through informed decisions and consistent attention translates to a healthier, happier, and more fulfilling companionship. Continued learning and adaptation to a dog’s evolving needs throughout its life ensures the highest quality of care and strengthens the unique connection shared between humans and their canine companions. This dedication to responsible canine care contributes to a more compassionate and humane world for all.