
Topical solutions designed for canine lacerations, abrasions, and other minor injuries typically contain antiseptic and cleansing agents to promote healing and prevent infection. These products are often formulated to be gentle on... Read more »
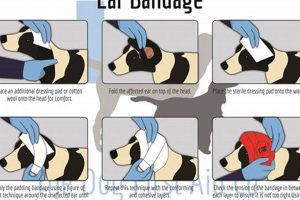
Managing auricular injuries in canines involves a range of procedures, from cleaning and dressing to administering medication and monitoring for infection. A simple scratch from a thorn bush or a more complex... Read more »

Protecting and treating injuries to the pads, toes, and nails of canines involves a range of practices. These practices encompass cleaning, bandaging, medication, and monitoring for infection. For instance, a simple cut... Read more »

This topical product combines a sulfonamide antibiotic with a soothing emollient base. Formulated specifically for canine skin, it provides antibacterial action while moisturizing and protecting affected areas. Similar products may utilize different... Read more »

Optimal canine wound management encompasses a range of practices, from initial assessment and cleaning to ongoing monitoring and treatment. For instance, a simple abrasion might require only antiseptic cleansing and a protective... Read more »
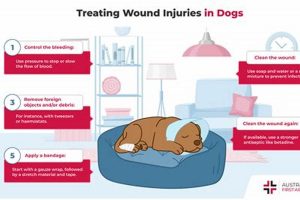
Proper wound management in canines involves a multi-step process designed to promote healing and prevent complications. This typically includes initial assessment, cleaning, disinfection, and, depending on severity, bandaging or other forms of... Read more »

Managing skin damage in canines that exposes underlying tissue requires prompt and appropriate treatment. This involves cleaning, protecting, and monitoring the affected area to promote healing and prevent complications such as infection.... Read more »

Various solutions designed for treating injuries in canines encompass items such as antiseptic washes, bandages, ointments, and specialized dressings. These supplies facilitate the healing process by cleansing the affected area, preventing infection,... Read more »
Pet supply retailers, such as PetSmart, often offer a range of products and services related to canine wound management. These can include antiseptic solutions, bandages, wound dressings, and sometimes even veterinary services.... Read more »

Injuries resulting from canine teeth can range from superficial abrasions to deep, penetrating trauma. These penetrating injuries, often characterized by small external wounds but potentially significant underlying tissue damage, necessitate specific attention... Read more »


