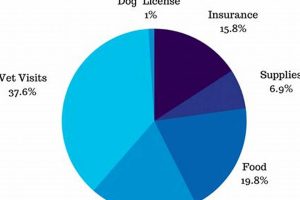
Caring for sled dogs encompasses a multifaceted approach addressing their unique physiological, psychological, and social needs. This includes providing appropriate nutrition, exercise, shelter, healthcare, and training. For instance, a proper diet for a working sled dog consists of high-protein, high-fat food, often supplemented with meat and fish. Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and parasite prevention are also crucial elements.
Maintaining the well-being of these animals is essential not only for their performance and longevity but also for upholding ethical standards in animal husbandry. Historically, sled dogs have played vital roles in transportation and exploration in arctic regions, fostering a deep bond between humans and animals. Their care has evolved alongside these partnerships, reflecting a growing understanding of their specific requirements.
The following sections will delve into the specific aspects of sled dog care, covering nutrition, exercise, shelter, health management, and training techniques in greater detail. This information is intended to provide a comprehensive guide for anyone involved in or interested in the proper maintenance of these remarkable animals.
Essential Tips for Sled Dog Care
Proper care is crucial for the health, happiness, and performance of sled dogs. These tips offer practical guidance for maintaining these remarkable animals.
Tip 1: Nutritional Needs: Provide a diet rich in protein and fat, tailored to activity levels. Dietary adjustments are necessary based on workload, climate, and individual metabolic needs. Fresh meat and fish can supplement commercial high-energy kibble.
Tip 2: Exercise Regimen: Regular and vigorous exercise is essential. Daily runs, even during the off-season, maintain physical condition and mental well-being. Varying terrain and distance prevent boredom and promote balanced muscle development.
Tip 3: Shelter and Housing: Provide adequate shelter from extreme weather conditions. Well-ventilated dog houses or insulated kennels with ample straw bedding offer protection from cold and wind. Access to shade is vital during warmer months.
Tip 4: Healthcare and Hygiene: Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and parasite prevention are paramount. Dental hygiene should also be prioritized. Inspect paws regularly for injuries and apply protective booties when necessary.
Tip 5: Socialization and Pack Dynamics: Understand and respect the social hierarchy within the pack. Introduce new dogs carefully and supervise interactions. Provide opportunities for socialization and play to promote harmonious pack dynamics.
Tip 6: Training and Commands: Consistent training using positive reinforcement establishes clear communication and control. Basic obedience commands and directional cues are essential for effective teamwork during runs.
Tip 7: Monitoring Health and Behavior: Observe dogs closely for changes in appetite, energy levels, or behavior. Early detection of potential health issues allows for prompt veterinary intervention and prevents complications.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures optimal physical and mental well-being for sled dogs, enabling them to thrive in their demanding roles. Proper care translates directly to improved performance, longevity, and a stronger bond between dog and handler.
By understanding and addressing the specific needs of these animals, one contributes to responsible animal husbandry and the preservation of these working dog traditions.
1. Nutrition
Optimal nutrition is fundamental to sled dog health, performance, and longevity. A carefully formulated diet provides the energy required for strenuous activity in demanding climates while supporting overall well-being and preventing health issues.
- Energy Balance
Maintaining appropriate energy balance is crucial. Caloric intake must match energy expenditure, which fluctuates based on workload, season, and individual metabolism. Insufficient caloric intake can lead to weight loss, fatigue, and compromised immune function, whereas excessive calories can result in obesity and related health problems. Calculations of energy requirements often consider factors like distance traveled, terrain, and ambient temperature.
- Macronutrient Ratio
Sled dogs require a diet rich in protein and fat. Protein supports muscle development and repair, essential for endurance. Fat provides a concentrated energy source crucial for sustained activity in cold environments. The optimal ratio of protein to fat varies depending on workload and individual needs. Diets typically consist of high-quality commercial dog food supplemented with meat, fish, or fat blends.
- Micronutrient Requirements
Ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals is vital for maintaining various physiological functions. These micronutrients support immune function, bone health, and overall metabolic processes. Dietary deficiencies can lead to health problems and reduced performance. Supplementation may be necessary to address specific needs based on individual assessments and dietary analysis.
- Hydration
Access to fresh, clean water is paramount, especially during periods of intense activity. Dehydration can impair performance and pose serious health risks. Water intake should be monitored regularly, and dogs should be encouraged to drink frequently. Providing warmed water during cold weather can prevent hypothermia and encourage adequate hydration.
By addressing these nutritional considerations, sled dog owners can optimize the health, performance, and longevity of their teams. A balanced and appropriate diet contributes significantly to their ability to thrive in challenging environments and perform demanding tasks while maintaining overall well-being.
2. Exercise
Regular and vigorous exercise is paramount for maintaining the physical and mental well-being of sled dogs. Their inherent need for activity necessitates a structured exercise regimen tailored to their breed, age, and individual conditioning. A proper exercise program not only sustains physical fitness but also prevents behavioral problems stemming from boredom and pent-up energy.
- Daily Runs
Consistent daily runs are fundamental. These runs should vary in distance and terrain to provide both physical and mental stimulation. Adapting the intensity and duration of runs to the season and individual dog’s condition is crucial. During the off-season, maintaining a base level of fitness prevents deconditioning and ensures a smooth transition into the working season. For example, shorter, less intense runs during the summer months help maintain muscle tone without overexertion in the heat.
- Strength and Endurance Training
Incorporating activities that build strength and endurance is essential for optimal performance. Weight pulling exercises, uphill runs, and swimming build muscle mass and improve cardiovascular fitness. These activities should be introduced gradually and adjusted according to each dog’s physical capabilities and progress. For instance, starting with lighter weights and gradually increasing the load helps prevent injuries and builds strength progressively.
- Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest and recovery are as important as the exercise itself. Providing ample downtime allows muscles to repair and rebuild, preventing overuse injuries and promoting overall health. Monitoring dogs for signs of fatigue, such as excessive panting or reluctance to exercise, allows for appropriate adjustments to the training regimen. Rest days should be incorporated strategically, particularly after strenuous activity.
- Mental Stimulation
Exercise provides not only physical but also crucial mental stimulation. The varied terrain and challenges encountered during runs engage their problem-solving skills and prevent boredom. Introducing new routes and incorporating activities like retrieving or scent work further enrich their environment and prevent behavioral issues associated with monotony. This contributes significantly to their overall well-being and contentment.
A well-structured exercise program contributes significantly to the overall health and well-being of sled dogs. By addressing their inherent need for physical activity, owners ensure not only optimal physical condition and performance but also prevent behavioral problems, foster a positive temperament, and strengthen the human-animal bond.
3. Shelter
Providing adequate shelter is a critical component of responsible sled dog care. These animals, adapted to cold climates, nonetheless require protection from extreme weather conditions, including wind, snow, rain, and excessive heat. Appropriate shelter contributes significantly to their overall health, well-being, and ability to perform. Exposure to harsh elements can lead to hypothermia, frostbite, heatstroke, and other health complications, impacting their ability to work and potentially shortening their lifespan. For example, during severe winter storms, a well-insulated dog house provides crucial protection from wind chill and heavy snowfall, preventing hypothermia and conserving energy.
Several factors influence the type of shelter best suited for sled dogs. Climate, breed characteristics, and individual dog preferences all play a role. In colder regions, insulated dog houses or kennels with ample dry bedding, such as straw, offer crucial protection. During warmer months, access to shade is essential to prevent overheating. Well-ventilated structures promote air circulation and prevent the buildup of moisture, which can contribute to respiratory problems and skin infections. Elevated platforms within the shelter keep dogs off the cold ground and provide a dry resting area. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the shelter prevent the accumulation of waste and minimize the risk of parasite infestations and disease transmission.
Providing effective shelter demonstrates a commitment to responsible sled dog care. This proactive approach not only safeguards their physical health but also enhances their overall comfort and well-being, ultimately contributing to their longevity and ability to thrive in demanding environments. Failure to provide adequate shelter can have serious consequences, jeopardizing their health and compromising their ability to perform the tasks for which they are bred. Therefore, careful consideration of shelter design and maintenance is essential for any individual or organization involved in the care of these remarkable animals.
4. Healthcare
Maintaining optimal health is crucial for sled dogs, given their demanding lifestyle and the often harsh environments they inhabit. Preventative healthcare, prompt diagnosis and treatment of illnesses, and ongoing monitoring are essential components of responsible sled dog care. A comprehensive healthcare approach contributes significantly to their well-being, longevity, and ability to perform at their best. Neglecting healthcare needs can lead to decreased performance, chronic health issues, and a diminished quality of life.
- Vaccinations and Parasite Control
Regular vaccinations protect against common canine diseases, such as rabies, distemper, and parvovirus. Parasite control, including prevention and treatment of fleas, ticks, worms, and other parasites, is equally vital. These parasites can transmit diseases, cause discomfort, and compromise overall health. Implementing a preventative healthcare schedule, tailored to the specific environment and risk factors, minimizes the likelihood of infections and infestations. For example, in regions with high tick populations, regular tick checks and preventative medications are essential.
- Dental Care
Dental health often gets overlooked but plays a significant role in a dog’s overall well-being. Regular dental checkups, professional cleanings, and at-home dental care, such as brushing and dental chews, help prevent periodontal disease, tooth decay, and other oral health issues. Poor dental hygiene can lead to pain, infection, and even systemic health problems. Addressing dental health proactively improves comfort, reduces the risk of complications, and contributes to long-term health. For instance, providing dental chews can help remove plaque and tartar buildup, promoting good oral hygiene.
- Injury Management
Sled dogs are prone to certain injuries, such as paw pad lacerations, muscle strains, and joint problems, due to the nature of their work. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of injuries are essential to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery. Regularly inspecting paws for cuts, abrasions, and foreign objects allows for early intervention and prevents minor injuries from becoming serious. Providing appropriate first aid and seeking veterinary care when necessary contribute significantly to their long-term health and ability to continue working. Applying protective booties during runs over rough terrain or in extreme cold can help prevent injuries.
- Geriatric Care
As sled dogs age, they may develop age-related health issues such as arthritis, hip dysplasia, and vision or hearing impairment. Providing appropriate geriatric care, including pain management, dietary adjustments, and adaptations to their exercise routine, ensures a comfortable and dignified retirement. Regular veterinary checkups become even more critical in older dogs to monitor for and manage age-related conditions effectively. Adapting their lifestyle to accommodate their changing needs allows them to enjoy their later years in comfort and maintain a good quality of life. This might involve providing orthopedic bedding or adjusting their exercise routine to include shorter, less strenuous walks.
Prioritizing healthcare in sled dog management ensures their overall well-being, maximizes their working lifespan, and fosters a strong bond between dog and handler. A comprehensive approach to healthcare, encompassing preventative measures, prompt diagnosis and treatment, and ongoing monitoring, demonstrates a commitment to responsible animal care and allows these remarkable animals to thrive in their demanding roles. By understanding and addressing their specific healthcare needs, owners contribute to a higher quality of life and enable these dogs to enjoy long, healthy, and productive lives.
5. Socialization
Socialization plays a vital role in the overall well-being of sled dogs. These animals, often working and living in close proximity, require careful integration and management of social dynamics within the pack. Proper socialization contributes significantly to their mental and emotional health, influencing behavior, performance, and the overall success of the team. Neglecting this aspect can lead to conflict, stress, and reduced effectiveness within the group. Understanding and managing pack dynamics is essential for anyone involved in their care.
- Pack Hierarchy
Sled dog packs naturally establish a social hierarchy, with dominant and subordinate individuals. This hierarchy provides structure and order within the group. Recognizing and respecting this hierarchy is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing conflict. Introducing new dogs carefully, observing interactions, and avoiding disruptions to the established order contribute to a harmonious pack environment. For example, introducing a new dog to the pack gradually, allowing them to interact under supervision, helps prevent aggression and facilitates integration into the existing social structure.
- Interaction and Play
Providing opportunities for positive social interaction and play is essential for sled dogs’ mental and emotional well-being. Play allows them to practice social skills, build bonds, and expend energy in a constructive manner. Supervised play sessions help prevent boredom, reduce stress, and promote positive relationships within the pack. This can include activities like tug-of-war, fetch, or simply allowing them to interact freely in a safe and controlled environment. Such interactions contribute significantly to their overall happiness and contentment.
- Integration of New Dogs
Introducing new dogs to an established pack requires careful management to avoid conflict and ensure smooth integration. Gradual introductions, under close supervision, allow existing pack members to acclimate to the new dog’s presence and establish their respective positions within the hierarchy. Monitoring interactions for signs of aggression or excessive dominance helps prevent escalation and promotes peaceful co-existence. This process may involve initially separating the new dog from the main pack, allowing them to become familiar with each other through scent and visual contact before gradually introducing them in controlled settings.
- Behavioral Issues and Intervention
Addressing behavioral issues promptly is crucial for maintaining a healthy pack dynamic. Aggression, excessive dominance, or fear-based behaviors can disrupt the social order and create stress within the group. Identifying the underlying causes of these behaviors, whether related to dominance struggles, resource guarding, or fear, allows for appropriate intervention strategies. Consulting with experienced trainers or behaviorists can provide valuable insights and guidance on addressing specific behavioral challenges effectively. This may involve implementing behavior modification techniques, adjusting pack management strategies, or providing additional socialization opportunities tailored to the specific needs of the individual dogs. Early intervention is key to preventing escalation and restoring balance within the pack.
Effective socialization practices are integral to responsible sled dog care. Understanding and managing pack dynamics, providing opportunities for positive interaction, and addressing behavioral issues promptly contribute significantly to the overall well-being of these animals. By fostering a harmonious and stable social environment, owners and handlers enhance the dogs physical and mental health, promote teamwork, and maximize their ability to thrive in their demanding roles. Proper socialization is not merely a matter of convenience; it is a fundamental aspect of ensuring their welfare and maximizing their potential.
6. Training
Training is an integral component of sled dog care, extending beyond basic commands to encompass the development of essential skills for teamwork, safety, and effective performance. A well-trained sled dog exhibits not only obedience but also the ability to navigate varied terrain, respond to directional cues, and work cooperatively within the team. This training contributes significantly to the safety of both the dogs and the handler, optimizing performance and minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries. Neglecting training can lead to control issues, decreased efficiency, and a potentially hazardous environment for all involved.
- Basic Obedience and Commands
Foundational obedience training establishes clear communication between the handler and the dogs. Commands such as “sit,” “stay,” “come,” and “no” provide a framework for control and responsiveness. This foundational training forms the basis for more advanced commands specific to sledding, such as directional cues (“gee” for right, “haw” for left) and speed control (“hike” to start, “whoa” to stop). Consistent reinforcement of these commands, using positive reinforcement techniques, ensures reliability and predictability in the dogs’ responses, crucial for safe and efficient sledding operations. For instance, a reliable “whoa” command is critical for stopping the team in emergencies or preventing accidents on challenging terrain.
- Harness and Line Training
Accustoming dogs to the harness and lines is a gradual process, starting with short periods and progressively increasing duration as they become comfortable. Proper harness fit is essential for comfort and injury prevention. Training includes teaching dogs to pull against the harness, working cooperatively in formation, and responding to directional commands while pulling. This training prepares them for the physical demands of sledding and ensures they can work effectively as a team. For example, dogs must learn to pull together in a coordinated manner to maximize efficiency and prevent tangling of the lines.
- Trail Etiquette and Safety
Trail etiquette encompasses training dogs to navigate various terrain, including snow, ice, and uneven surfaces. This involves teaching them to follow a designated trail, avoid obstacles, and respond appropriately to changing conditions. Safety training includes desensitization to distractions, such as wildlife encounters or passing vehicles, ensuring they remain focused on the task at hand and respond safely to unexpected situations. This aspect of training is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of both the dogs and the handler during runs. For instance, training dogs to remain calm and responsive in the presence of other animals or distractions on the trail enhances safety and prevents potentially dangerous reactions.
- Teamwork and Socialization During Training
Training often occurs in a group setting, providing opportunities for dogs to develop teamwork skills and reinforce appropriate social interactions. This allows them to learn to work cooperatively, respect the established pack hierarchy, and respond cohesively to commands as a unit. Observing and managing social dynamics during training sessions allows for early intervention in cases of conflict or dominance struggles, promoting a harmonious and efficient team dynamic. This approach reinforces the importance of working together towards a common goal, enhancing overall team performance and fostering a positive social environment within the pack. For example, training exercises that require dogs to work together to pull a weighted sled reinforce cooperation and build trust within the team.
Effective training is a continuous process, essential for maintaining discipline, enhancing performance, and ensuring the safety of both the dogs and the handler. It forms a cornerstone of responsible sled dog care, contributing significantly to their physical and mental well-being while enabling them to perform their tasks safely and efficiently. This investment in training translates directly to a more rewarding and successful sledding experience, fostering a stronger bond between handler and dogs while prioritizing their welfare and maximizing their potential.
7. Monitoring
Monitoring constitutes a crucial aspect of sled dog care, encompassing regular observation and assessment of individual animals’ physical and behavioral states. This ongoing process enables early detection of potential health issues, facilitates prompt intervention, and contributes significantly to maintaining overall well-being and preventing serious complications. Changes in appetite, energy levels, behavior, or physical condition can indicate underlying health problems, stress, or other concerns requiring attention. For instance, a sudden decrease in appetite coupled with lethargy could signal an infection, while changes in gait or posture might suggest musculoskeletal injury. The ability to recognize and interpret these subtle indicators allows for timely intervention, often mitigating the severity and duration of illness or injury.
Effective monitoring extends beyond visual observation to include regular weight checks, assessment of body condition score, and close attention to vital signs such as heart rate and respiratory rate. These quantitative measures provide valuable data for tracking trends and identifying deviations from normal baselines. For example, consistent weight loss despite maintaining food intake could indicate a metabolic issue, while an elevated resting heart rate might suggest underlying cardiac or respiratory problems. Integrating these objective measures with observed behavioral and physical changes provides a comprehensive picture of each dog’s health status, enabling more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies. Furthermore, detailed record-keeping of these observations facilitates communication with veterinarians and provides valuable historical data for tracking individual health trends over time.
Consistent and thorough monitoring is essential for proactive healthcare management, enabling timely intervention and promoting optimal health outcomes. This practice reduces the risk of complications, minimizes suffering, and contributes to the longevity and overall well-being of sled dogs. By recognizing the importance of monitoring as an integral part of responsible sled dog care, handlers demonstrate a commitment to providing the highest standard of care and ensuring the animals thrive in their demanding roles. The ability to detect subtle changes early allows for proactive intervention, preventing minor issues from escalating into major health crises and ensuring that these remarkable animals receive the care they need to lead long, healthy, and productive lives.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sled Dog Care
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the care and maintenance of sled dogs, providing concise and informative responses based on established best practices.
Question 1: What are the specific dietary requirements of sled dogs, especially during periods of intense activity?
Sled dogs require a diet rich in protein and fat, with increased caloric intake during periods of high activity. Specific formulations vary based on workload, climate, and individual metabolism, often involving high-energy kibble supplemented with meat, fish, or fat blends.
Question 2: How much exercise do sled dogs need, both during the working season and the off-season?
Regular exercise is essential year-round. Daily runs, adapted in intensity and duration to the season and individual conditioning, maintain physical fitness and prevent behavioral issues. Off-season exercise maintains a base level of fitness and ensures a smooth transition into the working season.
Question 3: What type of shelter is most appropriate for sled dogs, considering their adaptation to cold climates?
Well-ventilated, insulated dog houses or kennels provide optimal shelter. Ample dry bedding, such as straw, offers insulation against cold. Elevated platforms keep dogs off the cold ground. Access to shade is crucial during warmer months to prevent overheating.
Question 4: What are the key preventative healthcare measures essential for maintaining sled dog health?
Regular veterinary checkups, vaccinations, and parasite control are fundamental. Dental care, including regular brushing and professional cleanings, is also essential. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of injuries are crucial for long-term health and performance.
Question 5: How can one effectively manage the social dynamics within a sled dog pack, and what are the key considerations for introducing new dogs?
Understanding and respecting the established pack hierarchy is crucial. Introduce new dogs gradually under supervision, monitoring interactions closely. Provide opportunities for positive social interaction and play while addressing behavioral issues promptly.
Question 6: What are the essential components of a comprehensive training program for sled dogs, beyond basic obedience commands?
Training should encompass harness and line training, trail etiquette and safety procedures, and the development of teamwork skills. Directional commands and desensitization to distractions are crucial for safe and efficient sledding operations.
Addressing these frequently asked questions provides a foundation for understanding the multifaceted aspects of sled dog care. Prioritizing these considerations contributes significantly to the well-being, longevity, and optimal performance of these remarkable animals.
For further information and resources on sled dog care, consult reputable organizations dedicated to working dog welfare and connect with experienced mushers and veterinarians specializing in sled dog health.
Caring for Sled Dogs
Maintaining the well-being of sled dogs requires a multifaceted approach encompassing nutrition, exercise, shelter, healthcare, socialization, and training. Providing a balanced diet rich in protein and fat fuels their demanding lifestyle. Regular exercise maintains physical conditioning and mental stimulation, preventing boredom and behavioral issues. Appropriate shelter protects against harsh weather conditions, ensuring comfort and safety. Preventative healthcare, including vaccinations, parasite control, and dental care, safeguards their health and longevity. Careful management of social dynamics within the pack promotes harmonious relationships and effective teamwork. Consistent training, from basic obedience to specialized sledding commands, enhances performance and ensures safe operation. Regular monitoring enables early detection of potential health problems, facilitating prompt intervention and minimizing complications.
Proper care for sled dogs reflects a commitment to responsible animal husbandry and recognizes the unique contributions of these animals to human endeavors. This comprehensive approach ensures not only their physical health and longevity but also their mental and emotional well-being, enabling them to thrive in their demanding roles. Continued education and a dedication to best practices in animal care remain essential for preserving these remarkable working dog traditions and upholding ethical standards in their management.