Assistance provided to individuals with disabilities through the use of specifically trained canines encompasses a wide range of services. These animals are trained to perform tasks that mitigate the impact of physical, sensory, psychiatric, intellectual, and other disabilities. Examples include guiding individuals with visual impairments, alerting those with hearing impairments to sounds, retrieving dropped items, providing physical support and balance, and responding to medical emergencies like seizures. They can also offer invaluable emotional and psychological support, reducing anxiety and promoting independence.
The profound positive impact of this form of assistance on the lives of individuals with disabilities is well-documented. Increased independence, improved social integration, and enhanced emotional well-being are just some of the benefits. Historically, the use of working animals to aid humans dates back centuries, but the formal training and recognition of assistance canines evolved significantly during the 20th century, particularly after World War I. This evolution led to the development of standardized training practices, legal protections, and greater public awareness of the vital role these animals play.
The following sections will explore various aspects of canine assistance, including training methodologies, legal frameworks, and the ongoing advancements in this field. Further discussion will address the responsibilities of handlers, public etiquette surrounding working animals, and the significant contribution these partnerships make to fostering inclusivity and improving the quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
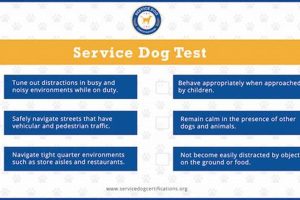
Tips for Interacting with Assistance Dogs
Appropriate interaction with assistance dog teams is crucial for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the working partnership. The following guidelines offer practical advice for navigating encounters with assistance dogs.
Tip 1: Do not distract the dog. Distractions can interfere with the dog’s concentration and ability to perform its duties. Avoid making direct eye contact, talking to, or petting the dog without explicit permission from the handler.
Tip 2: Ask before interacting. Always request permission from the handler before engaging with the dog. Respect the handler’s decision if permission is not granted.
Tip 3: Respect the dog’s space. Maintain a respectful distance and avoid crowding or startling the dog. These animals require personal space to perform their tasks effectively.
Tip 4: Do not offer food or treats. Assistance dogs follow specific dietary guidelines. Offering food or treats can disrupt their routines and potentially compromise their health.
Tip 5: Avoid making noises that might startle the dog. Sudden loud noises or high-pitched sounds can distract or frighten the dog. Maintain a calm and quiet demeanor when in proximity.
Tip 6: Be mindful of access needs. Understand that assistance dog teams have legal access rights to public spaces. Be considerate and accommodating of their needs.
Tip 7: Educate children on proper etiquette. Teach children the importance of respecting assistance dogs and how to interact appropriately, emphasizing the working role of these animals.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures the well-being and effectiveness of assistance dog teams, fostering a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with disabilities.
By understanding the role and importance of assistance dogs, one can contribute to a more accessible and inclusive society. The concluding section will reiterate key takeaways and emphasize the ongoing need for awareness and understanding of assistance dog etiquette.
1. Task Training
Task training is the cornerstone of service dog support, shaping the dog’s abilities to perform specific actions that directly address the handler’s disability-related needs. This specialized training is essential for fostering independence, enhancing safety, and improving overall quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
- Guiding and Mobility Support
For individuals with visual impairments, task training focuses on guiding through complex environments, navigating obstacles, and indicating changes in elevation. This includes halting at curbs, doorways, and intersections, ensuring safe traversal. These skills significantly enhance mobility and independence, allowing individuals to navigate the world with confidence.
- Medical Alert and Response
Service dogs can be trained to recognize and respond to specific medical events such as seizures, diabetic episodes, or allergic reactions. Training might involve alerting others to the situation, retrieving medication or medical devices, or providing deep pressure therapy to mitigate symptoms. This proactive response can be life-saving and provides crucial support during medical emergencies.
- Psychiatric Assistance
Task training for psychiatric service dogs focuses on supporting individuals with mental health conditions. Tasks may include interrupting harmful behaviors, creating personal space in crowded areas, retrieving medication, or providing grounding during anxiety or panic attacks. This support contributes to emotional stability and allows individuals to manage their conditions more effectively.
- Retrieval and Assistance with Daily Tasks
Individuals with physical disabilities benefit from task training that focuses on retrieving items, opening doors, turning on lights, assisting with dressing and undressing, and carrying objects. These tasks reduce reliance on others, promoting self-sufficiency and improving overall quality of life.
The multifaceted nature of task training underscores its vital role in service dog support. By tailoring training to specific disability-related needs, service dogs become indispensable partners, empowering individuals to live more independently and participate more fully in society. The diverse skills acquired through task training translate directly into tangible improvements in the lives of those they serve.
2. Disability Mitigation
Disability mitigation, a core component of service dog support, focuses on reducing the impact of functional limitations on an individual’s daily life. Service dogs are trained to perform specific tasks that directly address these limitations, enabling greater independence, participation, and overall well-being.
- Increased Mobility and Navigation
For individuals with physical or visual impairments, service dogs facilitate safe and independent movement. A dog trained to guide a person with visual impairments navigates obstacles, alerts to changes in elevation, and provides stability on uneven terrain. This support significantly reduces the risks associated with independent travel, expanding access to public spaces and fostering greater community engagement.
- Enhanced Sensory Awareness
Individuals with hearing impairments rely on service dogs to alert them to crucial auditory cues, such as doorbells, alarms, or approaching vehicles. This enhanced sensory awareness improves safety and facilitates communication within the environment, fostering greater independence and reducing reliance on others.
- Management of Medical Conditions
Service dogs trained to respond to medical episodes, such as seizures or diabetic emergencies, offer life-saving support. These dogs can be trained to alert others, retrieve medication, or provide deep pressure therapy, mitigating the severity of medical events and enhancing personal safety.
- Mitigation of Psychiatric Disabilities
Service dogs offer invaluable support to individuals with psychiatric disabilities by interrupting harmful behaviors, providing grounding during anxiety or panic attacks, and creating a sense of security in public spaces. These actions significantly mitigate the impact of psychiatric conditions, promoting emotional stability and enabling greater social engagement.
These examples illustrate how service dog support, through targeted task training, directly mitigates the impact of various disabilities. By reducing functional limitations, service dogs empower individuals to navigate daily life with increased independence, confidence, and overall well-being. This mitigation extends beyond physical tasks to encompass crucial emotional and psychological support, fostering greater inclusion and improving overall quality of life.
3. Increased Independence
Increased independence is a central benefit of service dog support, significantly impacting the lives of individuals with disabilities. By performing specific tasks, service dogs mitigate the challenges posed by physical, sensory, psychiatric, or intellectual limitations, empowering individuals to engage more fully in daily life and experience a greater sense of autonomy.
- Self-Reliance in Daily Tasks
Service dogs trained to retrieve items, open doors, assist with dressing, and perform other routine tasks reduce reliance on caregivers or family members. This newfound self-reliance fosters a sense of personal accomplishment and empowers individuals to manage daily routines with greater autonomy. For example, a service dog retrieving dropped medication enables an individual to manage their health independently, promoting self-sufficiency and reducing reliance on others.
- Enhanced Mobility and Access
Service dogs trained to guide individuals with visual impairments or provide stability for those with mobility challenges expand access to public spaces and community engagement. Navigating public transportation, accessing workplaces, and participating in social activities become more manageable and less daunting, fostering greater independence and social integration. The ability to navigate independently, without relying on others for guidance or assistance, significantly enhances an individual’s sense of freedom and control.
- Improved Safety and Security
Service dogs trained to alert to medical emergencies, provide deep pressure therapy during anxiety attacks, or interrupt harmful behaviors create a sense of safety and security, reducing the need for constant supervision or intervention. This enhanced safety net empowers individuals to engage in activities with greater confidence, knowing they have a reliable partner to assist them in challenging situations. For example, a service dog alerting to an oncoming seizure allows an individual to take preventative measures, minimizing risk and increasing personal safety.
- Greater Social Engagement
Service dogs often act as social facilitators, encouraging positive interactions and reducing social isolation. Their presence can initiate conversations, break down social barriers, and provide a sense of comfort in social situations. This increased social engagement contributes to improved emotional well-being and a greater sense of belonging within the community. The non-judgmental companionship of a service dog can also provide emotional support and reduce feelings of loneliness, contributing to a more fulfilling and independent life.
The increased independence fostered by service dog support has a profound impact on the overall well-being of individuals with disabilities. By mitigating the limitations imposed by disability, service dogs empower individuals to live more fulfilling lives, participate more actively in their communities, and experience a greater sense of autonomy and self-worth. This enhanced independence contributes not only to practical improvements in daily living but also to significant gains in emotional well-being, social integration, and overall quality of life.
4. Enhanced Social Integration
Enhanced social integration is a significant benefit derived from service dog support, often overlooked amidst the focus on practical assistance. The presence of a service dog can profoundly impact an individual’s social interactions, fostering connections, reducing social isolation, and promoting a greater sense of belonging within the community. This aspect of service dog support contributes significantly to overall well-being and quality of life.
- Reduced Stigma and Increased Understanding
Service dogs can act as natural conversation starters, providing opportunities for education and awareness about disabilities. These interactions can help dispel misconceptions and reduce stigma surrounding disabilities, fostering greater understanding and acceptance within the community. Through these interactions, individuals with disabilities may experience increased comfort and confidence in social settings.
- Facilitated Social Interaction and Connection
The presence of a service dog can create a bridge for social interaction, making it easier for others to approach and engage with the handler. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who experience social anxiety or difficulty initiating conversations. The dog’s presence can create a shared point of interest, fostering connections and reducing feelings of isolation. For example, a shared admiration for the dog’s training or appearance can spark conversations and create opportunities for social bonding.
- Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem
The constant companionship and unwavering support of a service dog can significantly boost an individual’s confidence and self-esteem. This increased self-assurance can translate to greater comfort and ease in social situations, empowering individuals to participate more actively in social activities and community events. The dog’s presence can provide a sense of security and reduce anxiety, allowing individuals to focus on social interaction rather than their disability or perceived limitations.
- Greater Access to Social Activities and Community Engagement
Service dogs facilitate access to a wider range of social activities and community events. Their presence mitigates accessibility challenges and provides a sense of security, enabling individuals to participate more fully in social gatherings, recreational activities, and community life. This increased participation fosters a stronger sense of belonging and connection within the community, reducing social isolation and promoting overall well-being. For example, a service dog can accompany an individual to a concert or sporting event, mitigating potential anxieties and enhancing the overall experience.
Enhanced social integration is a crucial aspect of service dog support, contributing significantly to the overall well-being and quality of life for individuals with disabilities. By fostering understanding, facilitating interaction, boosting confidence, and expanding access to social opportunities, service dogs play a vital role in promoting social inclusion and creating a more connected and supportive community. These social benefits complement the practical assistance provided by service dogs, creating a holistic support system that empowers individuals to thrive in all aspects of their lives.
5. Emotional Support
Emotional support, an often-underestimated facet of service dog support, plays a crucial role in the overall well-being of individuals with disabilities. While service dogs are widely recognized for their practical assistance, the emotional bond they provide offers significant psychological and emotional benefits, contributing to improved mental health, increased confidence, and a greater sense of security.
- Reduced Anxiety and Stress
The consistent presence of a service dog can significantly reduce anxiety and stress levels in individuals with disabilities. The dog’s calming presence, physical touch, and predictable behavior create a sense of stability and security, mitigating anxiety triggers and promoting emotional regulation. For example, a service dog trained to provide deep pressure therapy during anxiety attacks can offer immediate comfort and grounding, reducing the intensity and duration of the anxiety episode. This consistent emotional support can lead to improved mental health outcomes and a greater sense of overall well-being.
- Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem
Service dogs foster a sense of confidence and self-esteem in their handlers. The dog’s unwavering loyalty, non-judgmental companionship, and consistent support empower individuals to navigate social situations with greater ease and confidence. The dog’s presence can act as a social buffer, reducing self-consciousness and promoting positive social interactions. This increased confidence can extend beyond social settings, empowering individuals to pursue personal goals and engage more fully in daily life. For example, an individual with a service dog may feel more comfortable attending social gatherings or pursuing educational opportunities, leading to greater social inclusion and personal fulfillment.
- Mitigation of PTSD Symptoms
For individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), service dogs can offer invaluable emotional support. Trained to recognize and respond to signs of distress, these dogs can interrupt flashbacks, provide grounding techniques, and create a sense of safety and security. This specialized support can significantly mitigate PTSD symptoms, improving emotional regulation and reducing the frequency and intensity of traumatic episodes. The dog’s constant presence and predictable behavior can create a sense of stability and control, helping individuals navigate daily life with greater ease and confidence.
- Decreased Feelings of Loneliness and Isolation
Service dogs provide constant companionship, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation, particularly for individuals with mobility or social limitations. The dog’s presence offers unconditional love and support, fostering a deep emotional bond that combats social isolation and promotes a sense of belonging. This companionship can be particularly crucial for individuals living alone or those who experience difficulty forming social connections. The dog’s presence can fill a social void, providing emotional comfort and reducing feelings of loneliness and disconnection.
The emotional support provided by service dogs is integral to the comprehensive benefits they offer. This emotional bond, combined with practical assistance, creates a powerful synergy that significantly enhances the overall well-being, independence, and quality of life for individuals with disabilities. By addressing both the practical and emotional challenges associated with disability, service dogs empower individuals to thrive in all aspects of their lives. This holistic support underscores the profound impact of service dogs, extending far beyond the performance of specific tasks to encompass the essential emotional well-being of their handlers.
6. Public Access Rights
Public access rights are fundamental to the effectiveness of service dog support. These rights, enshrined in law, ensure that individuals with disabilities can access public spaces and services with their service dogs, thereby mitigating the limitations imposed by their disabilities and promoting full participation in society. This access is not merely a privilege but a crucial component of service dog support, enabling individuals to fully benefit from the assistance their dogs provide. Denying access effectively nullifies the support offered by the service dog, limiting independence and reinforcing societal barriers. For instance, an individual relying on a service dog for mobility would be unable to utilize public transportation or access a grocery store without guaranteed public access rights, significantly restricting their independence and community engagement. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of public access as an integral element of comprehensive service dog support.
The practical significance of public access rights is evident in various everyday scenarios. Individuals with service dogs rely on these rights to access workplaces, restaurants, stores, medical facilities, and other essential services. These rights ensure that individuals with disabilities can participate in the workforce, engage in social activities, and access healthcare without facing discriminatory barriers. Furthermore, public access rights promote social inclusion by normalizing the presence of service dogs in public spaces, fostering greater understanding and acceptance of individuals with disabilities. Consider the case of a student with a service dog attending university; without guaranteed access to classrooms, libraries, and other campus facilities, their ability to pursue education would be severely compromised. This exemplifies how public access rights are essential for individuals with service dogs to exercise their fundamental rights and participate fully in all aspects of society.
In conclusion, public access rights are not simply a legal provision but a cornerstone of effective service dog support. These rights are essential for ensuring that individuals with disabilities can fully realize the benefits of service dog partnerships, promoting independence, facilitating social integration, and fostering a more inclusive society. Challenges to these rights, whether through misinformation or discriminatory practices, directly undermine the purpose of service dog support and create significant barriers to full participation for individuals with disabilities. Upholding and protecting public access rights is therefore paramount to ensuring the efficacy and continued positive impact of service dog support within the community.
Frequently Asked Questions about Assistance Dog Support
This section addresses common inquiries regarding assistance provided by service dogs, aiming to clarify misconceptions and provide accurate information.
Question 1: What distinguishes a service dog from an emotional support animal or a therapy dog?
Service dogs are specifically trained to perform tasks directly related to an individual’s disability. Emotional support animals provide comfort and companionship but do not have specific task training. Therapy dogs are trained to provide comfort and affection in various settings, such as hospitals or nursing homes, but work with multiple individuals rather than a single handler. The distinction lies in the specific training and the nature of the support provided.
Question 2: What disabilities qualify for service dog support?
A wide range of disabilities, including physical, sensory, psychiatric, intellectual, and other medical conditions, can qualify for service dog support. The key criterion is whether the dog performs tasks that mitigate the impact of the disability, enhancing the individual’s ability to perform daily activities and participate in society. Eligibility is determined by the nature and impact of the disability, not the specific diagnosis.
Question 3: Where are service dogs permitted access?
Service dogs are generally permitted access to most public spaces, including businesses, transportation, and government buildings. Legal frameworks, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States, provide specific protections and access rights for individuals with service dogs. Access is granted based on the dog’s working status and its role in mitigating the handler’s disability, not based on the handler’s perceived need.
Question 4: How can one identify a legitimate service dog?
While no universally recognized identification is required for service dogs, their behavior and training typically distinguish them. Service dogs are generally well-behaved, focused on their handlers, and trained to perform specific tasks. Asking intrusive questions about the individual’s disability is discouraged. Focus should be on the dog’s behavior and whether it is actively engaged in tasks related to mitigating a disability.
Question 5: What are the responsibilities of a service dog handler?
Handlers are responsible for the dog’s care, including feeding, grooming, and veterinary care. They are also responsible for ensuring the dog’s behavior is appropriate for public spaces and that the dog’s presence does not pose a risk to others. This includes maintaining control of the dog and ensuring it is appropriately trained to perform its tasks reliably in public settings.
Question 6: Where can one find reputable service dog training organizations?
Reputable service dog training organizations adhere to established standards and prioritize the well-being of both the dogs and their future handlers. Organizations accredited by Assistance Dogs International (ADI) are generally considered reputable and follow rigorous training and ethical guidelines. Thorough research and careful consideration of training philosophies and practices are recommended when selecting a training organization.
Understanding the complexities of assistance dog support requires accurate information and awareness. This FAQ section aims to clarify common misconceptions and promote respectful interactions with service dog teams. Proper etiquette and consideration for the vital role these dogs play are crucial for creating an inclusive and accessible environment for individuals with disabilities.
For further information and resources, please consult the following section on accessible support organizations and informational websites.
Conclusion
This exploration of assistance dog support has highlighted its multifaceted nature, encompassing specialized task training, mitigation of disability-related challenges, increased independence, enhanced social integration, vital emotional support, and legally protected public access rights. Each facet contributes significantly to the overall well-being and quality of life for individuals with disabilities. From navigating complex environments to providing crucial emotional stability, the impact of these highly trained canines extends far beyond practical assistance. The examination of public access rights underscored the essential legal framework that enables individuals with service dogs to participate fully in society, highlighting the interconnectedness of legal protections and effective assistance dog support.
Continued advocacy for public awareness, education regarding proper etiquette around service dog teams, and ongoing advancements in training methodologies are essential for ensuring the continued effectiveness and accessibility of assistance dog support. Broader societal understanding of the profound impact these partnerships have on fostering independence and inclusion remains crucial for creating a more accessible and equitable future for individuals with disabilities. The invaluable contributions of service dogs underscore the transformative power of these partnerships, enriching not only the lives of those they serve but also the fabric of our communities as a whole.