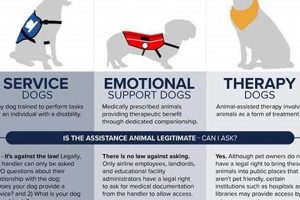
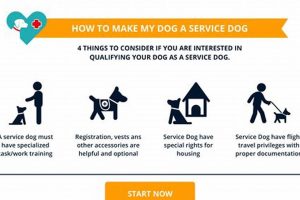
Canine education involves developing desired behaviors in dogs, often through positive reinforcement techniques like rewarding good behavior with treats or praise. This process can range from basic obedience commands (sit, stay, come) to more complex actions and specialized skills such as service work or scent detection. A well-executed program establishes clear communication and expectations between human and animal.
Educated canines contribute positively to society as well-behaved companions, assistance animals, and working partners. This education fosters stronger human-animal bonds, improves canine welfare by reducing anxiety and promoting mental stimulation, and enhances public safety by mitigating behavioral issues that could lead to unwanted incidents. Throughout history, humans have developed various methodologies for shaping canine conduct, reflecting evolving understandings of animal learning and cognition.
The following sections delve deeper into specific aspects of canine education, covering topics such as choosing appropriate training methods, understanding canine learning principles, addressing common behavioral challenges, and selecting qualified instructors.
Tips for Effective Canine Education
Successful canine education relies on consistency, patience, and an understanding of canine behavior. These tips provide guidance for achieving positive outcomes.
Tip 1: Start Early. Early socialization and training during puppyhood establish a foundation for lifelong good behavior. Introducing puppies to various environments, sounds, and experiences builds confidence and adaptability.
Tip 2: Use Positive Reinforcement. Rewarding desired behaviors with treats, praise, or toys motivates dogs to repeat those actions. Positive reinforcement fosters a positive learning experience and strengthens the human-animal bond.
Tip 3: Be Consistent. Consistent application of training techniques and commands helps dogs understand expectations clearly. Inconsistency can lead to confusion and hinder progress.
Tip 4: Keep Training Sessions Short and Engaging. Short, frequent training sessions maintain a dog’s focus and prevent boredom. Engaging activities make learning enjoyable and increase motivation.
Tip 5: Address Problem Behaviors Early. Addressing unwanted behaviors promptly prevents them from becoming ingrained habits. Professional guidance may be beneficial for addressing complex behavioral issues.
Tip 6: Socialize Regularly. Regular interaction with other dogs and people helps dogs develop appropriate social skills. Socialization is crucial for preventing fear and aggression.
Tip 7: End on a Positive Note. Concluding each training session with a successful exercise builds confidence and leaves a positive impression. This approach encourages continued engagement in future training sessions.
Implementing these tips cultivates well-behaved canine companions, strengthens human-animal bonds, and promotes a harmonious relationship between humans and their canine companions.
By focusing on these core principles, individuals can achieve effective and lasting results in canine education, fostering a positive and rewarding experience for both the dog and the owner.
1. Methods
Method selection significantly impacts canine education outcomes. Effective methods leverage canine learning principles, focusing on positive reinforcement, clear communication, and consistency. Aversive methods, relying on punishment or intimidation, can negatively impact canine welfare, potentially leading to fear, anxiety, and aggression. Positive reinforcement, such as rewarding desired behaviors with treats or praise, strengthens the human-animal bond while motivating the dog to repeat those behaviors. For example, teaching a dog to sit using a treat as a reward when the dog performs the desired action, reinforces the behavior effectively and humanely. Conversely, using harsh corrections can create fear and distrust, hindering the learning process and potentially damaging the relationship between dog and owner. Choosing the right method is crucial for achieving training goals and ensuring the dog’s well-being.
Different training methods cater to various learning styles and behavioral needs. Clicker training, a positive reinforcement method using a distinct sound to mark desired behaviors, facilitates precise communication and accelerates learning. Classical conditioning, associating a neutral stimulus with a specific response, can be employed to modify emotional responses, such as reducing fear or anxiety. Operant conditioning, focusing on the consequences of behavior, shapes actions through reinforcement or punishment. Understanding the principles underlying each method allows for informed selection and application tailored to the individual dog’s temperament and training goals. Integrating multiple compatible methods can create a comprehensive training approach that optimizes learning and addresses specific challenges.
Effective method implementation requires consistency, patience, and observation. Consistency reinforces expectations and facilitates learning. Patience allows dogs to progress at their own pace, minimizing frustration. Careful observation enables trainers to recognize subtle cues from the dog, adjusting methods as needed to optimize learning and address any emerging challenges. Selecting and applying appropriate methods, while considering the individual dog’s characteristics and learning style, forms the cornerstone of successful canine education. This approach fosters a positive learning environment, strengthens the human-animal bond, and promotes well-adjusted canine companions.
2. Timing
Effective canine education hinges on appropriate timing. Precisely when training interventions occur significantly influences learning outcomes. Understanding the importance of timing allows for optimized training strategies that maximize learning potential and foster positive behavioral development.
- Developmental Stages
Different developmental stages present unique opportunities and challenges for learning. Puppyhood represents a critical period for socialization and foundational training. Adolescence often brings about hormonal changes and increased independence, requiring adjustments in training approaches. Adult dogs may require different training strategies compared to puppies, focusing on refining existing skills or addressing specific behavioral issues. Adapting training to the dog’s developmental stage optimizes learning and addresses age-specific needs.
- Immediacy of Feedback
Providing immediate feedback, whether positive reinforcement or redirection, strengthens the association between behavior and consequence. Delayed feedback reduces the effectiveness of training interventions, as the dog may not connect the feedback to the specific behavior. For example, rewarding a dog immediately after it performs a desired action reinforces that action more effectively than delayed praise or reward. The immediacy of feedback is crucial for effective learning and behavior modification.
- Duration and Frequency
Training sessions should be kept short and frequent to maintain the dog’s focus and engagement. Lengthy sessions can lead to boredom and frustration, hindering learning. Multiple short sessions distributed throughout the day prove more effective than infrequent, prolonged training. Adjusting the duration and frequency of training sessions to the individual dog’s attention span and learning style optimizes knowledge retention and prevents mental fatigue.
- Contextual Relevance
The timing of training within specific contexts influences its effectiveness. Training a dog to “stay” in a quiet environment differs significantly from practicing the same command in a distracting setting. Gradually introducing distractions and varying training environments enhances generalization and ensures the dog can perform the desired behavior reliably in real-world situations. Contextual relevance strengthens the practical application of learned behaviors.
By considering these facets of timing, canine education becomes more effective, yielding positive outcomes. Appropriate timing maximizes learning potential, strengthens the human-animal bond, and promotes well-adjusted canine companions. Understanding the interplay between timing and learning enhances training methodologies and contributes to successful behavior modification.
3. Consistency
Consistency forms the bedrock of effective canine education. It provides the clarity and predictability dogs require for successful learning. Without consistent application of training principles, dogs become confused, hindering progress and potentially leading to behavioral issues. Consistent training encompasses various aspects, including clear communication, consistent application of rules and boundaries, and consistent use of reinforcement strategies.
Consistent communication entails using the same verbal cues and hand signals for specific commands. For example, always using the word “sit” and the accompanying hand gesture ensures the dog understands the desired action. Changing cues or using different words for the same behavior creates confusion and slows down the learning process. Consistent application of rules and boundaries means maintaining the same expectations for behavior in various situations. If a dog is not allowed on furniture, this rule should apply consistently, regardless of visitors or location. Inconsistency in enforcing rules creates ambiguity and encourages the dog to test boundaries. Similarly, consistent reinforcement strategies, such as rewarding desired behaviors with treats or praise, strengthen the association between the action and the reward. Inconsistent reinforcement weakens this association, making it harder for the dog to understand what is expected.
Consistent application of these principles fosters a predictable learning environment, enabling dogs to understand expectations clearly. This clarity accelerates learning, strengthens the human-animal bond, and promotes a harmonious relationship. Conversely, inconsistency breeds confusion, potentially leading to frustration, anxiety, and undesirable behaviors. Understanding the pivotal role of consistency in canine education equips owners with the tools to establish clear communication, build trust, and achieve lasting training outcomes.
4. Socialization
Socialization plays a crucial role in canine development, directly impacting training outcomes. It involves exposing dogs to various stimuli, environments, and social interactions, shaping their behavior and adaptability. Effective socialization contributes significantly to well-adjusted, confident canines, fostering positive interactions with humans and other animals. This process lays the groundwork for successful training by reducing fear, anxiety, and aggression, enabling dogs to learn more effectively.
- Early Exposure
Early exposure to diverse stimuli during puppyhood proves critical for healthy development. Introducing puppies to various sights, sounds, surfaces, and experiences builds resilience and adaptability. Early socialization experiences, such as controlled introductions to other dogs, people of different ages and appearances, and novel environments, lay the foundation for confident adult dogs. This early exposure minimizes the likelihood of fear-based behaviors and facilitates easier training.
- Social Interaction
Regular, positive social interaction with other dogs is essential for developing appropriate social skills. Controlled play sessions with well-socialized dogs teach puppies bite inhibition, communication, and social etiquette. These interactions help prevent inappropriate social behaviors, such as aggression or fear, which can interfere with training. Positive social experiences contribute to well-adjusted dogs capable of navigating social situations confidently.
- Environmental Adaptation
Exposure to different environments, including urban settings, rural areas, and various indoor spaces, prepares dogs for real-world situations. Encountering different surfaces, noises, and visual stimuli reduces anxiety and promotes adaptability. This environmental desensitization makes training more effective, as dogs are less likely to be distracted or fearful in novel situations. A well-adapted dog responds better to commands and learns more readily in various environments.
- Human Interaction
Positive interactions with a variety of humans are crucial for socialization. Exposing dogs to people of different ages, genders, and appearances helps them develop appropriate responses to unfamiliar individuals. Gentle handling and positive reinforcement during these interactions build trust and reduce the likelihood of fear or aggression. Positive human interaction is fundamental for creating well-adjusted dogs that integrate seamlessly into human society and respond positively to training.
These facets of socialization contribute significantly to a dog’s overall well-being and trainability. A well-socialized dog exhibits reduced anxiety and fear, making them more receptive to learning and less likely to develop behavioral problems. By fostering positive social experiences and exposing dogs to a wide range of stimuli, socialization enhances the effectiveness of training, promoting well-adjusted canine companions capable of thriving in diverse environments.
5. Reinforcement
Reinforcement serves as a cornerstone of effective canine education. It shapes behavior by associating actions with consequences, motivating dogs to repeat desired behaviors. Understanding the principles of reinforcement is crucial for achieving training goals and fostering a positive learning experience.
- Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement involves adding something desirable, such as a treat, praise, or toy, immediately after a dog performs a desired behavior. This positive association motivates the dog to repeat the behavior. For example, rewarding a dog with a treat after it successfully sits strengthens the association between the command “sit” and the action of sitting. Positive reinforcement builds a positive learning experience, strengthens the human-animal bond, and encourages continued engagement in training.
- Negative Reinforcement
Negative reinforcement involves removing an aversive stimulus, such as pressure from a leash or a loud noise, when a dog performs a desired behavior. This relief reinforces the behavior. For example, releasing leash pressure when a dog walks politely on a loose leash encourages the dog to continue walking politely to avoid the pressure. It is important to distinguish negative reinforcement from punishment; negative reinforcement removes an unpleasant stimulus, while punishment adds an unpleasant stimulus. When used correctly, negative reinforcement can be an effective training tool, but it requires careful application to avoid causing fear or anxiety.
- Timing and Consistency
The timing and consistency of reinforcement significantly impact its effectiveness. Reinforcement delivered immediately after a desired behavior strengthens the association most effectively. Delayed reinforcement weakens the connection, making it harder for the dog to understand what is being rewarded. Consistency in applying reinforcement, meaning rewarding the desired behavior every time it occurs, especially during initial learning, accelerates the learning process and establishes clear expectations. Inconsistent reinforcement can lead to confusion and hinder progress.
- Reinforcement Schedules
Different reinforcement schedules influence how quickly a behavior is learned and how resistant it is to extinction. Continuous reinforcement, rewarding the behavior every time it occurs, leads to rapid learning but also rapid extinction if the reinforcement stops. Intermittent reinforcement, rewarding the behavior only sometimes, leads to slower learning but greater resistance to extinction. Varying reinforcement schedules, such as randomly rewarding the behavior, can maintain high levels of motivation and prevent the dog from becoming dependent on constant rewards.
Understanding and applying these principles of reinforcement is essential for successful canine education. Choosing the right type of reinforcement, delivering it consistently and with appropriate timing, and utilizing effective reinforcement schedules contribute significantly to achieving training goals, building a positive relationship between dog and owner, and fostering a well-behaved and well-adjusted canine companion. Effective reinforcement strengthens desirable behaviors, reduces undesirable behaviors, and enhances communication between human and animal, forming the foundation of a successful training program.
6. Communication
Effective communication forms the cornerstone of successful canine education. Clear and consistent communication bridges the gap between human intentions and canine understanding, enabling effective learning and a strong human-animal bond. Without clear communication, training becomes challenging, potentially leading to frustration for both the dog and the owner. Understanding canine communication methods and utilizing appropriate human communication strategies is essential for successful training outcomes.
- Verbal Cues
Verbal cues, such as commands like “sit,” “stay,” and “come,” provide clear instructions to the dog. Using consistent verbal cues, avoiding variations in phrasing or tone, helps dogs associate specific words with desired actions. For example, consistently using the word “sit” paired with the hand gesture for sit helps the dog learn the command reliably. Clear and consistent verbal cues are fundamental for establishing clear expectations.
- Nonverbal Cues
Nonverbal cues, including body language, hand gestures, and facial expressions, communicate subtle messages to dogs. Maintaining a calm and assertive posture conveys confidence and leadership, while avoiding sudden or erratic movements helps prevent startling or confusing the dog. Using clear hand signals in conjunction with verbal cues enhances communication, particularly for dogs who may have difficulty hearing or who are visually oriented. Consistent and intentional use of nonverbal cues complements verbal communication, creating a comprehensive communication strategy.
- Understanding Canine Communication
Recognizing and interpreting canine communication signals is crucial for effective training. Dogs communicate through body language, vocalizations, and facial expressions. Understanding these signals allows owners to anticipate the dog’s emotional state, adjust training approaches as needed, and avoid misinterpretations that could lead to unintended consequences. For example, recognizing signs of stress or anxiety, such as lip licking, yawning, or whale eye, indicates the need to adjust the training approach or provide a break. Sensitivity to canine communication enhances the effectiveness of training and strengthens the human-animal bond.
- Consistency and Timing
Consistency in communication, both verbal and nonverbal, is essential for clarity. Using the same cues consistently, delivering them with clear timing, and avoiding mixed signals helps dogs understand expectations reliably. Timing is equally crucial; providing feedback immediately after a behavior strengthens the association between the action and the consequence. Delayed feedback reduces the effectiveness of communication, making it harder for the dog to connect the feedback to the specific behavior. Consistent and well-timed communication fosters clear understanding and promotes successful learning outcomes.
These facets of communication form the foundation of effective canine education. By utilizing clear and consistent verbal and nonverbal cues, understanding canine communication signals, and delivering feedback with precise timing, trainers establish a clear line of communication with their canine companions. This clarity fosters trust, accelerates learning, and strengthens the human-animal bond, contributing to well-behaved, well-adjusted dogs capable of thriving in various environments.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Education
This section addresses common inquiries regarding canine education, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What is the optimal age to commence canine education?
While basic socialization can begin as early as a few weeks old, formal training generally starts around eight weeks. Early socialization and training establish a foundation for lifelong learning and adaptable behavior.
Question 2: How long does it typically take to observe results?
The timeframe for observable results varies depending on the individual dog, the complexity of the behavior being taught, and the consistency of training. Generally, noticeable progress can be observed within a few weeks of consistent training.
Question 3: Are certain breeds more amenable to training than others?
While some breeds exhibit predispositions towards certain tasks or learning styles, all breeds are capable of learning with appropriate training methods. Individual temperament, rather than breed alone, often plays a more significant role in trainability.
Question 4: What are the most effective training methods for canines?
Positive reinforcement methods, rewarding desired behaviors with treats, praise, or toys, are widely recognized as the most effective and humane training approaches. These methods foster a positive learning environment and strengthen the human-animal bond.
Question 5: How can one address common behavioral issues like excessive barking or leash pulling?
Addressing behavioral issues requires understanding the underlying cause of the behavior. Consulting with a certified professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide tailored guidance and strategies for behavior modification.
Question 6: How important is socialization in canine education?
Socialization is crucial for developing well-adjusted canines. Exposing dogs to various environments, people, and other animals during critical developmental periods helps them develop appropriate social skills and reduces the likelihood of fear-based behaviors, facilitating easier training and integration into society.
Consistent training, utilizing positive reinforcement and clear communication, yields optimal results in canine education. Addressing individual needs and seeking professional guidance when necessary contributes significantly to success.
The subsequent sections delve further into specific training techniques and address common challenges encountered in canine education.
Conclusion
Canine education, encompassing a spectrum from basic obedience to specialized skills, proves essential for fostering well-adjusted companions and contributing to societal harmony. Methodologies grounded in positive reinforcement, coupled with consistent communication and a keen understanding of canine behavior, yield optimal outcomes. The significance of early socialization, addressing developmental stages, and adapting training approaches to individual needs remains paramount throughout the educational journey. Effective implementation of these principles strengthens the human-animal bond, mitigates behavioral issues, and promotes responsible canine ownership.
Continued exploration and refinement of canine education practices hold profound implications for enhancing canine welfare and further integrating canines into human society. Investing in evidence-based training methods and promoting responsible ownership practices benefits both individual dogs and the broader community. Cultivating a deeper understanding of canine behavior and learning principles paves the way for more effective communication and stronger, more enriching human-animal relationships.