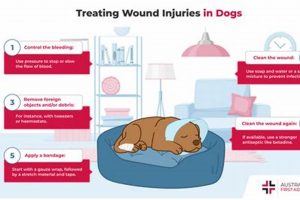
Providing optimal care for a Labrador Retriever involves a multifaceted approach encompassing various aspects of the dog’s well-being. This includes providing proper nutrition, regular exercise, consistent training, and routine healthcare. For example, a balanced diet formulated for a Labrador’s specific needs, coupled with daily walks and playtime, contributes significantly to their physical health. Consistent training, beginning in puppyhood, establishes clear boundaries and fosters a strong bond between dog and owner, while regular veterinary check-ups ensure early detection and prevention of potential health issues.
Appropriate canine husbandry practices lead to a healthier, happier, and longer lifespan for Labradors. These practices minimize the risks of breed-specific health issues such as hip and elbow dysplasia, obesity, and certain eye conditions. Historically, Labradors were bred for physically demanding tasks like retrieving game, requiring robust health and stamina. Maintaining a focus on their physical and mental well-being honors this heritage and allows these intelligent and energetic dogs to thrive in modern domestic environments.
The following sections will delve into the specific requirements of Labrador care, covering topics such as nutrition, exercise, training, grooming, health management, and creating a safe and enriching environment.
Tips for Labrador Care
Effective Labrador care requires attention to detail and a proactive approach. The following tips offer practical guidance for maintaining the health and well-being of these intelligent and energetic dogs.
Tip 1: Nutritional Needs: Provide a high-quality diet formulated for large breed dogs, considering factors such as age, activity level, and any specific health conditions. Avoid overfeeding, as Labradors are prone to obesity. Portion control and scheduled feeding times are crucial.
Tip 2: Exercise Requirements: Labradors possess abundant energy and require regular exercise to maintain physical and mental health. Daily walks, runs, swims, and engaging play sessions are essential. Incorporate activities that challenge their intelligence, such as retrieving games.
Tip 3: Training and Socialization: Begin training and socialization early in puppyhood. Consistent, positive reinforcement methods work best. Exposure to various environments, people, and other dogs promotes well-adjusted behavior.
Tip 4: Grooming Essentials: Regular grooming maintains a Labrador’s coat health and prevents matting. Weekly brushing is typically sufficient. Regularly check ears for cleanliness and trim nails as needed.
Tip 5: Healthcare: Schedule routine veterinary check-ups for vaccinations, parasite prevention, and early detection of potential health issues. Discuss breed-specific health concerns, such as hip and elbow dysplasia, with a veterinarian.
Tip 6: Environmental Enrichment: Provide a safe and stimulating environment. Labradors thrive on interaction and require mental stimulation. Offer a variety of toys, puzzles, and opportunities for social interaction.
Tip 7: Dental Care: Regular dental hygiene is essential. Brush a Labradors teeth regularly using a canine-specific toothpaste. Dental chews and toys can also help maintain oral health.
By adhering to these guidelines, one can ensure the long-term health, happiness, and well-being of a Labrador Retriever, fostering a strong bond and enriching the lives of both dog and owner.
In conclusion, responsible Labrador ownership demands commitment and understanding of the breed’s specific needs. Implementing these tips contributes significantly to a fulfilling and rewarding relationship with these loyal and affectionate companions.
1. Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in the overall health and well-being of a Labrador Retriever. A balanced diet directly impacts a Labrador’s energy levels, coat health, joint function, and lifespan. Optimal nutrition requires careful consideration of the dog’s age, activity level, and any existing health conditions. For example, a growing puppy requires a diet higher in protein and calories than an adult dog. Similarly, a senior Labrador benefits from a diet formulated for joint health and weight management. Neglecting proper nutrition can lead to obesity, joint problems, digestive issues, and a compromised immune system. Providing appropriate nutrition is therefore a cornerstone of responsible Labrador care.
Practical application of nutritional principles involves selecting high-quality dog food formulated for a Labrador’s specific needs. Reading and understanding pet food labels is crucial. Ingredients should be listed in descending order of predominance by weight. Meat-based protein sources should be listed first, followed by whole grains and vegetables. Avoiding fillers, artificial colors, and excessive amounts of by-products contributes to a healthier diet. Portion control is also essential. Overfeeding, even with healthy food, can lead to obesity. Consulting a veterinarian for personalized dietary recommendations ensures a Labrador receives the optimal nutrition for their individual circumstances.
In summary, providing a balanced and appropriate diet is fundamental to Labrador care. A nutritional strategy tailored to a dog’s individual needs supports healthy growth, maintains ideal weight, promotes joint health, and contributes to a longer, happier life. Understanding the connection between nutrition and a Labrador’s overall well-being empowers owners to make informed decisions about their dog’s dietary needs and contributes significantly to responsible pet ownership.
2. Exercise
Exercise forms a cornerstone of Labrador Retriever care, directly impacting both physical and mental well-being. Bred for physically demanding tasks, Labradors possess inherent energy and drive that necessitate regular physical activity. A lack of sufficient exercise can manifest in behavioral issues such as destructiveness, excessive barking, and anxiety. Conversely, a well-exercised Labrador exhibits improved temperament, reduced stress levels, and better overall health. For example, a daily vigorous walk or run can significantly reduce a Labrador’s propensity to engage in destructive chewing. Furthermore, regular exercise contributes to maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related health problems, including joint issues and diabetes.
The practical application of exercise in Labrador care involves incorporating a variety of activities into the dog’s routine. Daily walks, runs, swims, and retrieving games cater to the breed’s natural inclinations and provide both physical and mental stimulation. The intensity and duration of exercise should be adjusted according to the dog’s age and health status. Puppies, for instance, require shorter, less strenuous activity periods compared to adult dogs. Senior Labradors may benefit from low-impact activities such as swimming or gentle walks. Furthermore, incorporating activities that engage the dog’s intelligence, like scent work or agility training, provides mental enrichment and reinforces the human-animal bond. Providing opportunities for social interaction with other dogs during exercise further enhances their well-being.
In conclusion, adequate exercise is not simply a component of Labrador care, but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the breed’s physical and mental health. Understanding the link between exercise and well-being, and implementing a practical exercise regimen tailored to individual needs, is crucial for responsible Labrador ownership. Neglecting a Labrador’s need for exercise can have detrimental consequences, while prioritizing regular physical activity contributes significantly to a healthier, happier, and more balanced companion.
3. Training
Training forms an integral component of Labrador Retriever care, directly influencing the dog’s behavior, well-being, and integration into human society. A well-trained Labrador exhibits desirable behaviors, fostering a harmonious relationship with its owner and enhancing the dog’s overall quality of life. Conversely, a lack of training can result in undesirable behaviors such as jumping, excessive barking, and pulling on the leash, leading to frustration for both dog and owner. Consistent, positive reinforcement training establishes clear communication and boundaries, promoting a sense of security and predictability for the dog. For example, a Labrador trained to respond reliably to recall commands enjoys greater freedom and reduces the risk of accidental injury or escape. Furthermore, training provides mental stimulation, channeling the breed’s intelligence and eagerness to please into productive activities. This mental engagement contributes to a more contented and well-adjusted dog.
Practical application of training principles involves starting early in puppyhood and utilizing positive reinforcement methods. Rewarding desired behaviors with treats, praise, or toys reinforces positive associations and motivates the dog to repeat those behaviors. Consistency and patience are crucial, as Labradors, while intelligent and eager to please, require repetition and positive reinforcement to solidify learned behaviors. Addressing undesirable behaviors through redirection and positive reinforcement, rather than punishment, fosters a trusting relationship and encourages desired responses. Enrolling in obedience classes provides structured learning opportunities and professional guidance, facilitating effective training practices. Furthermore, incorporating training into everyday interactions, such as mealtimes and playtime, reinforces learned commands and strengthens the bond between dog and owner.
In conclusion, training is not merely a desirable aspect of Labrador care but an essential element of responsible ownership. A well-trained Labrador exhibits improved behavior, enjoys greater freedom, and experiences a higher quality of life. Understanding the significance of training and implementing effective training methods contribute substantially to a harmonious relationship between dog and owner, ensuring a fulfilling and enriching experience for both. Neglecting training can lead to behavioral challenges and diminish the potential for a positive human-animal bond, while prioritizing training fosters a well-adjusted, well-behaved, and happy companion.
4. Grooming
Grooming constitutes a significant aspect of Labrador Retriever care, contributing directly to the dog’s hygiene, health, and overall well-being. Regular grooming practices maintain coat health, prevent skin issues, and provide opportunities for early detection of potential health problems. Furthermore, grooming sessions offer a chance to strengthen the bond between dog and owner through positive interaction and tactile stimulation. Neglecting grooming can lead to matting, skin infections, and discomfort for the dog, underscoring the importance of incorporating regular grooming into a comprehensive care regimen.
- Coat Care:
Labrador Retrievers possess a double coat consisting of a dense, water-resistant outer coat and a soft, insulating undercoat. Regular brushing, typically weekly, removes loose hair, prevents matting, and distributes natural oils, maintaining coat health and shine. During shedding seasons, more frequent brushing may be necessary. Regular brushing also minimizes the amount of loose hair deposited around the home.
- Bathing:
While frequent bathing is not necessary, occasional baths help remove dirt and debris. Using a dog-specific shampoo formulated for sensitive skin prevents dryness and irritation. Thorough rinsing ensures complete removal of shampoo residue, preventing skin issues. Drying the coat thoroughly after bathing prevents matting and chilling.
- Ear Care:
Regular ear checks and cleaning prevent ear infections, a common issue in Labradors due to their drop ears. Cleaning the ears with a veterinarian-approved solution removes wax and debris, reducing the risk of infection. Observing for signs of redness, swelling, or discharge warrants veterinary attention.
- Nail Trimming:
Regular nail trimming prevents overgrowth, which can cause discomfort and difficulty walking. Trimming nails too short can cause bleeding and pain, so caution and appropriate tools are necessary. If uncomfortable trimming nails, consulting a veterinarian or professional groomer offers a safe alternative.
In conclusion, incorporating these grooming practices into a regular routine contributes significantly to a Labrador Retriever’s overall health, hygiene, and comfort. Regular grooming not only maintains the dog’s physical well-being but also strengthens the human-animal bond through positive interaction. Integrating grooming into a comprehensive care plan demonstrates responsible ownership and ensures a Labrador Retriever thrives in a healthy and caring environment.
5. Healthcare
Healthcare constitutes a critical component of responsible Labrador Retriever ownership, directly impacting the dog’s longevity, quality of life, and overall well-being. A proactive approach to healthcare, encompassing preventative measures, routine check-ups, and prompt attention to emerging health concerns, mitigates the risk of serious illness and contributes to a healthier, happier life for the dog. Implementing a comprehensive healthcare plan demonstrates a commitment to the dog’s welfare and reflects responsible pet ownership. For instance, regular vaccinations protect against preventable diseases such as canine distemper and parvovirus, safeguarding the dog’s health and preventing the spread of these diseases within the canine population. Similarly, routine parasite prevention protects against heartworm, fleas, and ticks, preventing discomfort, disease transmission, and potential long-term health complications.
Practical application of healthcare principles involves establishing a relationship with a qualified veterinarian. Regular check-ups, typically annually or biannually, facilitate early detection of potential health issues. These check-ups provide opportunities for vaccinations, parasite prevention, dental care, and overall health assessments. Open communication with a veterinarian regarding any observed changes in the dog’s behavior, appetite, or physical condition enables prompt diagnosis and treatment of emerging health concerns. Furthermore, understanding breed-specific health predispositions, such as hip and elbow dysplasia in Labrador Retrievers, allows for proactive monitoring and management of these conditions. Early intervention often improves outcomes and minimizes the long-term impact of these conditions on the dog’s quality of life. Addressing dental health through regular brushing and professional cleanings prevents dental disease, a common issue in dogs that can lead to pain, infection, and other health complications.
In conclusion, prioritizing healthcare is not simply a component of Labrador care, but an essential responsibility of ownership. A proactive and comprehensive approach to healthcare, encompassing preventative measures, routine veterinary care, and prompt attention to health concerns, ensures a Labrador Retriever receives the best possible care throughout its life. Neglecting healthcare can have significant consequences for the dog’s health and well-being, while prioritizing preventative care and timely interventions contributes significantly to a longer, healthier, and more fulfilling life for these loyal and beloved companions. Understanding the crucial role of healthcare in overall Labrador care empowers owners to make informed decisions that promote the dog’s long-term health and happiness.
6. Enrichment
Enrichment constitutes a crucial aspect of Labrador Retriever care, directly impacting the dog’s mental and emotional well-being. Providing a stimulating and engaging environment prevents boredom, reduces stress, and promotes balanced behavior. Labradors, renowned for their intelligence and energetic nature, require mental stimulation to thrive. A lack of enrichment can manifest in destructive behaviors, excessive barking, and anxiety. Conversely, a well-enriched environment fosters a contented, well-adjusted dog, strengthening the human-animal bond and enhancing overall quality of life. For example, providing puzzle toys challenges a Labrador’s problem-solving skills, preventing boredom and channeling their energy into productive activities.
- Mental Stimulation:
Mental stimulation forms the core of enrichment, engaging a Labrador’s cognitive abilities and preventing boredom. Puzzle toys, interactive games, and training sessions challenge the dog’s problem-solving skills and provide a healthy outlet for their intelligence. Examples include treat-dispensing toys, hide-and-seek games, and learning new tricks. Mental stimulation contributes to a more contented and well-adjusted Labrador, reducing the likelihood of destructive behaviors stemming from boredom or frustration.
- Physical Enrichment:
Physical enrichment complements mental stimulation, providing opportunities for exploration, exercise, and sensory engagement. Walks in new environments, access to varied terrains, and opportunities for swimming or retrieving satisfy a Labrador’s inherent need for physical activity and exploration. For example, a walk in a park with varied scents and textures provides greater sensory input than a walk on a familiar paved path. Physical enrichment contributes to both physical and mental well-being.
- Social Interaction:
Social interaction plays a vital role in Labrador enrichment, fulfilling the breed’s inherent social needs. Regular interaction with other dogs, whether through playdates, dog parks, or group training classes, provides opportunities for socialization and play. Positive social interactions contribute to a Labrador’s emotional well-being and reduce the risk of developing social anxieties or aggression. Supervised play sessions with well-socialized dogs offer valuable opportunities for learning appropriate social behaviors.
- Sensory Enrichment:
Sensory enrichment expands a Labrador’s experiential world, stimulating their senses and promoting mental engagement. Introducing new scents, textures, sounds, and sights provides novel experiences that prevent boredom and stimulate curiosity. Examples include providing toys with different textures, playing nature sounds, or introducing new, safe objects for exploration. Sensory enrichment adds variety and interest to a Labrador’s environment, promoting mental alertness and preventing sensory deprivation.
In conclusion, providing adequate enrichment is not merely a supplemental aspect of Labrador care, but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the breed’s mental and emotional well-being. Integrating a diverse range of enrichment activities into a Labrador’s daily routine contributes significantly to a balanced, well-adjusted, and contented companion. Neglecting enrichment can have detrimental consequences for the dog’s behavior and overall happiness, while prioritizing enrichment activities fosters a stimulating and fulfilling life, strengthening the human-animal bond and enriching the lives of both dog and owner. Understanding the crucial role of enrichment in overall Labrador care empowers owners to create an environment that nurtures the dog’s natural curiosity, intelligence, and inherent need for mental and physical stimulation.
7. Socialization
Socialization represents a crucial aspect of Labrador Retriever care, profoundly influencing the dog’s behavioral development, emotional well-being, and successful integration into human society. Appropriate socialization during formative periods establishes a foundation for positive interactions with other dogs, humans, and various environments, mitigating the risk of behavioral issues stemming from fear, anxiety, or aggression. Neglecting socialization can result in a dog that exhibits fear-based aggression, reactivity to novel stimuli, and difficulty adapting to new situations. Conversely, a well-socialized Labrador exhibits confidence, adaptability, and appropriate social skills, fostering harmonious relationships with its environment and enriching its overall quality of life.
- Early Exposure:
Early exposure to diverse stimuli during puppyhood forms the cornerstone of effective socialization. Introducing a Labrador puppy to a variety of sights, sounds, smells, people, and other dogs during this critical developmental period establishes a foundation for positive associations and reduces the likelihood of fear-based reactions later in life. For instance, exposing a puppy to different surfaces, such as grass, concrete, and gravel, desensitizes them to varying textures and prevents anxieties related to unfamiliar ground. Early exposure lays the groundwork for a confident and well-adjusted adult dog.
- Positive Interactions:
Positive interactions with other dogs are essential for developing appropriate social skills and preventing canine aggression. Supervised play sessions with well-socialized dogs allow Labrador puppies to learn canine communication cues, establish appropriate play behaviors, and develop healthy social dynamics. Positive interactions contribute to a dog’s emotional well-being and reduce the risk of social anxieties or aggression. For example, observing appropriate play bowing and other canine communication signals helps a puppy understand and respond appropriately to social cues from other dogs.
- Human Interaction:
Positive interactions with humans of various ages, appearances, and genders are equally crucial for socialization. Exposing a Labrador puppy to a diverse range of people helps them develop comfort and confidence around humans, preventing fear-based reactions or aggression. Gentle handling, positive reinforcement, and exposure to different social situations, such as encountering people in wheelchairs or using assistive devices, foster a well-adjusted dog comfortable interacting with a wide range of individuals. This broad exposure contributes to a Labrador’s successful integration into human society.
- Environmental Adaptation:
Adaptability to various environments constitutes a key component of socialization. Exposing a Labrador to different locations, such as parks, busy streets, and veterinary clinics, desensitizes them to novel stimuli and prevents anxieties related to unfamiliar surroundings. Gradual exposure to these environments, coupled with positive reinforcement, helps the dog develop confidence and adaptability, reducing the likelihood of stress or fear in new situations. This adaptability enhances the dog’s ability to navigate and enjoy a variety of environments throughout its life.
In conclusion, socialization plays a pivotal role in shaping a Labrador Retriever’s behavior, temperament, and overall well-being. Integrating a comprehensive socialization plan into early puppyhood and continuing throughout the dog’s life contributes significantly to a well-adjusted, confident, and socially adept companion. Neglecting socialization can have detrimental consequences, limiting the dog’s ability to interact comfortably with its environment and potentially leading to behavioral issues. Prioritizing socialization, however, fosters a well-rounded, adaptable, and emotionally healthy Labrador, enriching the human-animal bond and ensuring a fulfilling life for both dog and owner. A well-socialized Labrador exhibits confidence, enjoys positive interactions with its surroundings, and thrives in the company of both humans and other dogs, demonstrating the profound impact of socialization on overall canine welfare.
Frequently Asked Questions about Labrador Retriever Care
This section addresses common queries regarding Labrador Retriever care, offering practical insights and guidance for prospective and current owners.
Question 1: What are the specific dietary requirements of a Labrador Retriever?
Labrador Retrievers require a balanced diet formulated for large breed dogs, with protein sources, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. Dietary needs vary based on age, activity level, and health status. Consulting a veterinarian for personalized recommendations is advised.
Question 2: How much exercise does a Labrador Retriever need?
Labradors require substantial daily exercise, typically a minimum of one hour, including walks, runs, or active playtime. Adequate exercise prevents obesity, reduces behavioral issues, and promotes physical and mental well-being.
Question 3: What are the most effective training methods for Labrador Retrievers?
Positive reinforcement methods, rewarding desired behaviors with treats or praise, are generally most effective. Consistency, patience, and early socialization are crucial for successful training.
Question 4: How often should a Labrador Retriever be groomed?
Weekly brushing maintains coat health and minimizes shedding. Bathing should occur as needed, typically every few months or when the coat becomes dirty. Regular ear cleaning and nail trimming are also essential grooming practices.
Question 5: What are the common health concerns associated with Labrador Retrievers?
Labradors are predisposed to certain health issues, including hip and elbow dysplasia, obesity, and certain eye conditions. Regular veterinary check-ups, appropriate exercise, and a balanced diet mitigate these risks.
Question 6: How can a stimulating and enriching environment be created for a Labrador Retriever?
Providing a variety of toys, puzzles, and opportunities for social interaction and physical activity prevents boredom and promotes mental stimulation. Regular walks in different environments, interactive games, and training sessions contribute to a stimulating and enriching environment.
Addressing these common queries provides a foundation for understanding the core principles of Labrador Retriever care. Implementing these guidelines contributes significantly to the dog’s overall well-being and fosters a strong, positive relationship between dog and owner.
For further information, consult reputable sources such as veterinary professionals, breed-specific organizations, and canine behavioral specialists.
How to Take Care of a Labrador Dog
Optimal Labrador Retriever care necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing physical well-being, mental stimulation, and responsible ownership practices. Adequate nutrition fuels energy levels and supports overall health. Regular exercise, including walks, runs, and interactive play, maintains physical and mental fitness while mitigating behavioral issues. Consistent training, beginning in puppyhood, establishes clear communication and reinforces desired behaviors. Routine grooming, including brushing, bathing, and nail trimming, ensures hygiene and allows for early detection of potential health concerns. Preventative healthcare, such as vaccinations and regular veterinary check-ups, safeguards against diseases and promotes long-term well-being. Finally, a stimulating environment, rich with opportunities for mental and physical enrichment, prevents boredom and fosters a contented, well-adjusted companion.
Commitment to these principles promotes a fulfilling life for Labrador Retrievers, enriching the human-animal bond and fostering a harmonious relationship between dog and owner. Diligent application of these care guidelines contributes significantly to the dog’s physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life, underscoring the profound impact of responsible ownership on canine welfare. Prioritizing these aspects of care ensures Labradors thrive as healthy, happy, and well-adjusted companions, strengthening the unique bond between humans and these loyal, affectionate dogs.